추천 제품
애플리케이션
Human carbonic anhydrase II has been used in a study to assess quantitative imaging of mitochondrial and cytosolic free zinc levels in an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion. Human carbonic anhydrase II has also been used in a study to investigate a new scrubber concept for catalytic CO2 hydration.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
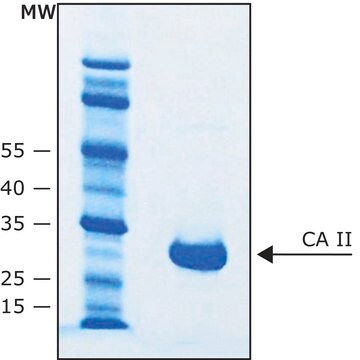
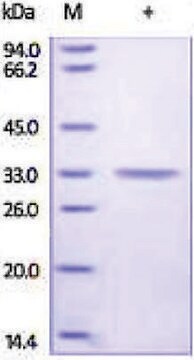
Carbonic anhydrase is a zinc metalloenzyme that catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to carbonic acid. It is involved in vital physiological and pathological processes such as pH and CO2 homeostasis, transport of bicarbonate and CO2, biosynthetic reactions, bone resorption, calcification, and tumorigenicity. It is required for renal acidification. Its absence can lead to osteoporosis, renal tubular acidosis, and cerebral calcification. Therefore, this enzyme is an important target for inhibitors with clinical applications in glaucoma, epilepsy and Parkinson′s disease. In addition, it is being explored as a potential target for obesity and cancer. CAII has a molecular mass of approximately 30 kDa and is primarily present in type II pneumocytes. Due to this unique location it has been speculated that CAII is involved in pulmonary functions such as regulation of fluid secretion and facilitation of CO2 elimation. Sulfonamides, sulfamates and sulfamides are potent inhibitors of CA.
단위 정의
One Wilbur-Anderson (W-A) unit will cause the pH of a 0.02 M Trizma buffer to drop from 8.3 to 6.3 per min at 0 °C. (One W-A unit is essentially equivalent to one Roughton-Booth unit.)
물리적 형태
Supplied as a solution in 20 mM Tris, pH 7.5, with 150 mM NaCl.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
시험 성적서(COA)
Lot/Batch Number
이미 열람한 고객
Md Abdur Razzak et al.
Frontiers in plant science, 11, 563721-563721 (2020-12-18)
Carbonic anhydrase (CA; EC 4.2.2.1) is a Zn-binding metalloenzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration of CO2. Recently, CAs have gained a great deal of attention as biocatalysts for capturing CO2 from industrial flue gases owing to their extremely fast reaction
New scrubber concept for catalytic CO2 hydration by immobilized carbonic anhydrase II and in-situ inhibitor removal in three-phase monolith slurry reactor
Iliuta, I. and F. Larachi
Separation and Purification Technology, 86, 199-214 (2012)
Bryan J McCranor et al.
Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes, 44(2), 253-263 (2012-03-21)
The role of zinc ion in cytotoxicity following ischemic stroke, prolonged status epilepticus, and traumatic brain injury remains controversial, but likely is the result of mitochondrial dysfunction. We describe an excitation ratiometric fluorescence biosensor based on human carbonic anhydrase II
Screening and docking studies of natural phenolic inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase II
Huang HQ, et al.
Science in China. Series B, Chemistry, Life Sciences & Earth Sciences, 52(3), 332-337 (2009)
Samira Ranjbar et al.
International journal of biological macromolecules, 50(4), 910-917 (2012-02-22)
This study reports the interaction between furosemide and human carbonic anhydrase II (hCA II) using fluorescence, UV-vis and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Fluorescence data indicated that furosemide quenches the intrinsic fluorescence of the enzyme via a static mechanism and hydrogen
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.