05-369
Anti-Na+/K+ ATPase α-1 Antibody, clone C464.6
clone C464.6, Upstate®, from mouse
Synonym(s):
ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 3 polypeptide, Na(+)/K(+) ATPase alpha(III) subunit, Na(+)/K(+) ATPase alpha-3 subunit, Na+/K+ -ATPase alpha 3 subunit, Na+/K+ ATPase 3, Sodium pump subunit alpha-3, dystonia 12, sodium pump 3, sodium-potassium-ATPase,
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
C464.6, monoclonal
species reactivity
rabbit, monkey, sheep, mouse, Xenopus, human, pig, canine, rat
packaging
antibody small pack of 25 μg
manufacturer/tradename
Upstate®
technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG1κ
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... ATP1A3(478)
Related Categories
General description
In order to maintain the cell potential, cells must keep a low concentration of sodium ions and high levels of potassium ions within the cell (intracellular). Outside cells (extracellular), there are high concentrations of sodium and low concentrations of potassium, so diffusion occurs through ion channels in the plasma membrane. In order to keep the appropriate concentrations, the sodium-potassium pump pumps sodium out and potassium in through active transport.
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
2 µg of a previous lot immuno-precipitated the α-1 subunit from rat brain microsomal preparations.
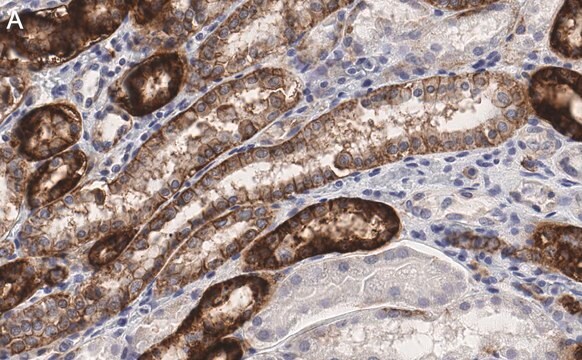
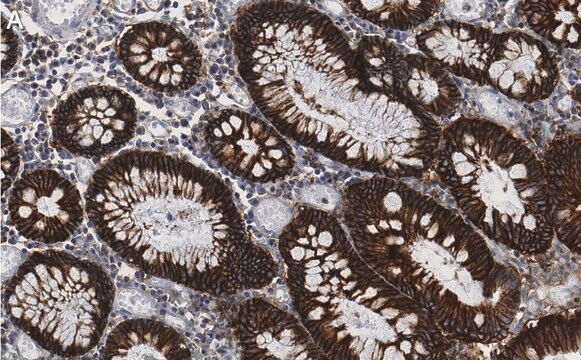
Immunohistochemistry:
1-10 µg/mL of a previous lot of this antibody was used in immunohistochemistry on ice-cold methanol-fixed tissue.
1. Do not boil microsomes. Warming to 37ºC for 15 minutes is recommended.
2. Microsomes from some tissues may contain sodium pump subunits which are below the level of detection by this antibody.
3. Microsomes derived from tissues which are more difficult to prepare, such as smooth and skeletal muscle, frequently show non-specific cross-reactivity.
Neuroscience
Ion Channels & Transporters
Quality
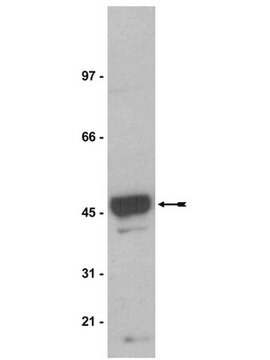
Western Blot Analysis:
0.05-0.1 µg/mL of this lot detected the α-1 subunit in 20 µg of rat brain microsomal preparation (Catalog # 12-144). To reduce background, wash the blot with 0.05% Tween-20 in PBS for 15 minutes.
Target description
Physical form
-20ºC.
Produced from a culture supernatant of a hybridoma produced by fusing Ag8 mouse myeloma cells with immunized Balb/c splenocytes. Clone C464.6 also called 6H.
Storage and Stability
Handling Recommendations:
Upon receipt, and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
Analysis Note
Alpha 1 mRNA is present in all cell types examined.
Other Notes
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service