추천 제품
생물학적 소스
mouse
Quality Level
항체 형태
purified immunoglobulin
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
131-14871, monoclonal
AH4H7-1, monoclonal
종 반응성(상동성에 의해 예측)
all
제조업체/상표
Chemicon®
기술
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
동형
IgG1
배송 상태
wet ice
관련 카테고리
일반 설명
특이성
면역원
애플리케이션
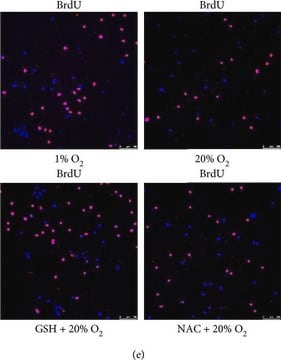
Flow Cytometry: (0.2 μg/100 μl/10E6 cells) Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
APPLICATIONS
Flow cytometry:The method below is based on that of M. Vanderlaan et al. (1986). Variations of this method exist in the literature, one consideration being the effect various fixation procedures have on the light-scattering properties of different cell populations. Procedure:
1. To label cells, pulse with 10 μM bromodeoxyuridine for 30 minutes. Harvest cells from culture.
2. Fix cells in 70% ethanol at +2-8°C for at least 30 min. Extract histones by resuspending cells in 1 mL chilled 0.1 M HCI containing 0.5% Triton X-100; incubate the suspension on ice for 10 minutes. Dilute acid with 5 mL distilled water and centrifuge at 200 x g for 10 min. Resuspend cells in 2 mL distilled water.
3. Denature cellular DNA by submerging the cell suspension into a boiling water bath for 10 min. Afterwards, quickly cool by placing the cell suspension in an ice slurry for several minutes. Wash cells in PBS that contains 0.5% Triton X-100.
4. Resuspend the cells (1-2 x 10 6 cells) in 100 μL of solution containing approximately 2 μg/mL anti-bromodeoxyuridine antibody diluted in PBS containing 0.1% BSA (0.2 μg/test). Incubate for 30 min at room temperature. Wash cells with PBS.
5. Resuspend cells in 100 μL of diluted goat anti-mouse IgG-FlTC Wash cells with PBS.
APPLICATIONS (Cont.)
Immunohistochemistry: Below is a procedure for staining cells that have been labeled with BrdU in vivo or in vitro. The procedure is based on the methods of B. Schutte et al. (1987) and D. Campana et al. (1988).
Preparation of tissue:
Inject animal with 50 mg BrdU/kg body weight. Sacrifice animal one hour later and remove organ or tissue under study. Embed tissue in OCT medium and snap-freeze by immersion into liquid nitrogen.Cut 4 mm frozen sections with a cryostat. Place sections on either albumin- or gelatin-coated slides.
Preparation of cells:
Pulse cells with 10 mM BrdU for 60 min. Cells grown on coverslips, or cytocentrifuge preparations made from cells grown in suspension, can be used for anti-bromodeoxyuridine staining according to the procedure below.
Procedure
1. Fix tissue sections or cells (on slide or coverglass) by immersing in absolute methanol for 10 minutes at +2-8°C. Air dry after removing from fixative. The slides can be stored at -20°C in a sealed box, or rehydrated to prepare for the assay procedure. To rehydrate, immerse in PBS for 3 min.
2. Denature DNA by incubating the slides in 2 N HCI for 60 min at +37°C.
3. Neutralize the acid by immersing the slides in 0.1 M borate buffer, pH 8.5. Change the buffer twice over a 10 min period.
4. Wash slides with PBS, changing the solution three times over a 10 min period.
5. Place slides in a humidified chamber (e.g., a sealed plastic box layered with wet paper towels) and cover cells with 150-300 μL of solution containing approximately 6 μg/mL anti-bromodeoxyuridine antibody diluted in PBS with 0.1% BSA. Incubate for 60 min at room temperature.
6. Wash slides with PBS, changing the solution three times over a 10 min period.
7. Apply optimal dilution of a second antibody conjugate (e.g., anti-mouse IgG-peroxidase), incubate, wash, and perform detection with a substrate that produces an insoluble product. After detection, counterstain with Harris-modified hematoxylin if desired. Slides can then be dehydrated and mounted.
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Cell Cycle, DNA Replication & Repair
표적 설명
결합
물리적 형태
저장 및 안정성
분석 메모
After incorporation of BrdU, all DNA containing species
기타 정보
법적 정보
면책조항
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.