Separation with Cytiva Products (GST Fusion Proteins)
Glutathione S-transferase (GST) is one of the most common tags used to facilitate the purifcation and detection of recombinant proteins and a range of products for simple, one step purifcation of GST fusion proteins are available (see Purifcation options).
Purifcation and detection of GST-tagged proteins, together with information on how to handle fusion proteins when they are expressed as inclusion bodies, are dealt with in depth in the GST Gene Fusion System Handbook and The Recombinant Protein Handbook: Protein Amplication and Simple Purifcation, available from Cytiva.
Purifcation Options |
|---|
* See Appendix 4 to convert linear flow (cm/h) to volumetric flow rate. Maximum operating flow is calculated from measurement in a packed column with a bed height of 10 cm and i.d. of 5 cm.
Purification Examples
Figure 22 shows a typical purification of GST fusion protein on GSTrap FF 1 ml with an SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified protein.
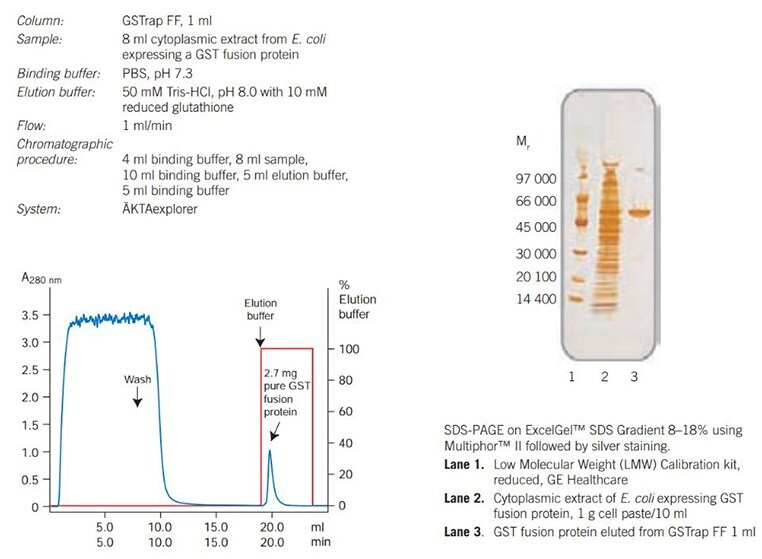
Figure 22.Purification of a GST fusion protein.
Figure 23 shows how the purification of a GST fusion protein can be scaled up 20-fold from a GSTrap FF 1 ml column to a GSTPrep FF 16/10 column.

Figure 23. Scaling up purifcation of a GST fusion protein.
Performing a Separation
Binding buffer: 140 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.3
Elution buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM reduced glutathione, pH 8.0
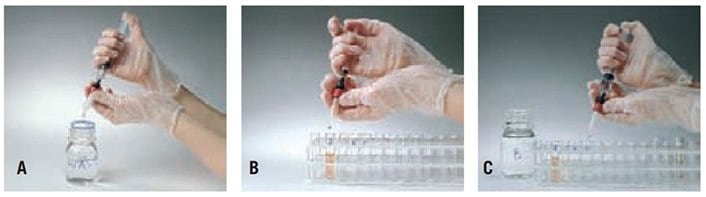
Figure 24. Using GSTrap FF with a syringe. A: Prepare buffers and sample. Remove the column’s top cap and twist off the end. B: Equilibrate column, load the sample and begin collecting fractions. C: Wash and elute, continuing to collect fractions.
- Equilibrate the column with 5 column volumes of binding buffer.
- Apply the sample.
- Wash with 5–10 column volumes of binding buffer.
- Elute with 5–10 column volumes of elution buffer.
- Wash with 5–10 column volumes of binding buffer.
It is important to keep a low flow rate during sample loading and elution as the kinetics of the binding interaction between GST and glutathione are relatively slow. The binding capacity is protein dependent and therefore yield will vary according to the type of protein. Yield may be improved by using a slower flow rate or passing the sample through the column several times.
For a single purification of a small quantity of product or for high throughput screening, GST MicroSpin columns are convenient and simple to use with either centrifugation or MicroPlex 24 Vacuum.
To increase capacity, connect several GSTrap FF columns (1 ml or 5 ml) in series. For greater capacity, use GSTPrep 16/10 FF columns or pack Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow into a suitable column (see Appendix 3, Column packing and preparation for affinity chromatography). GSTrap FF columns can be used with a syringe, a peristaltic pump or a chromatography system.
Enzyme-specific recognition sites are often included to allow the removal of the GST tag by enzymatic cleavage when required. Thrombin is commonly used for enzymatic cleavage, and must, subsequently, be removed from the recombinant product. HiTrap Benzamidine FF (high sub) 1 ml or 5 ml columns provide simple, ready-made solutions for this process (see page 54, Purifcation or removal of serine proteases, e.g. thrombin and trypsin, and zymogens).
Reuse of GSTrap FF depends on the nature of the sample. To prevent cross-contamination, columns should only be reused with identical samples.
Cleaning
These procedures are applicable to Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow and Glutathione Sepharose 4B.
- Wash with 2–3 column volumes of alternating high pH (0.1 M Tris-HCl, 0.5 M NaCl, pH 8.5) and low pH (0.1 M sodium acetate, 0.5 M NaCl, pH 4.5) buffers.
- Repeat the cycle 3 times.
- Re-equilibrate immediately with 3–5 column volumes of binding buffer.
If the medium is losing binding capacity, this may be due to an accumulation of precipitated, denatured or non-specifically bound proteins.
To remove precipitated or denatured substances:
- Wash with 2 column volumes of 6 M guanidine hydrochloride.
- Wash immediately with 5 column volumes of binding buffer.
To remove hydrophobically bound substances:
- Wash with 3–4 column volumes of 70% ethanol (or 2 column volumes of a non-ionic detergent (Triton™ X-100 1%)).
- Wash immediately with 5 column volumes of binding buffer.
Media Characteristics |
|---|
Chemical Stability
No significant loss of binding capacity when exposed to 0.1 M citrate (pH 4.0), 0.1 M NaOH, 70% ethanol or 6 M guanidine hydrochloride for 2 hours at room temperature. No significant loss of binding capacity after exposure to 1% SDS for 14 days.
Storage
Wash media and columns with 20% ethanol at neutral pH (use approximately 5 column volumes for packed media) and store at +4 to +8 °C.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?