おすすめの製品
由来生物
mouse
品質水準
抗体製品の状態
ascites fluid
抗体製品タイプ
primary antibodies
クローン
3C4, monoclonal
化学種の反応性
human
メーカー/製品名
Chemicon®
テクニック
electron microscopy: suitable
flow cytometry: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
アイソタイプ
IgG1κ
NCBIアクセッション番号
UniProtアクセッション番号
輸送温度
dry ice
ターゲットの翻訳後修飾
unmodified
遺伝子情報
human ... COL6A3(1293)
詳細
ヒトでは、コラーゲンアルファ-3(VI)鎖(UniProt P12111;コラーゲンVIアルファ-3ポリペプチドとも呼ばれる)は、COL6A3遺伝子(Gene ID 1293)がコードしています。VI型コラーゲンは、軟骨、骨、腱、筋肉、角膜などのほぼ全ての結合組織に存在する細胞外マトリックス(ECM)の成分であり、基底膜と密接に関連したミクロフィブリルを形成します。筋肉の基底膜と細胞周囲マトリックスを固定することに加えて、コラーゲンVIがシグナル伝達と細胞遊走において何らかの役割を果たしていることも研究で示されています。コラーゲンVIの基礎的な構造単位は、アルファ-1(VI)、アルファ-2(VI)、アルファ-3(VI)鎖(それぞれ、COL6A1、COL6A2、COL6A3遺伝子がコードする)から成るヘテロ三量体です。α1(VI)およびα2(VI)鎖は大きさとドメイン構造がほぼ同じで、すべてのコラーゲンに特徴的な335または336アミノ酸の三重ヘリックス領域を含んでいます。三重ヘリックスに隣接して、フォンウィルブランド因子のA型ドメイン(VWAドメイン)と相同なドメインがあります。α1(VI)およびα2(VI)は、三重ヘリックス(N1)のN末端の1つのVWAドメインと、ヘリックスのC末端の2つのVWAドメイン(C1およびC2)を持っています。一方、α3(VI)鎖は大型であり、10個のN末端VWAドメイン(N1–N10)と2個のC末端VWAドメイン(C1およびC2)を持ち、C末端領域にいくつかのその他のタイプの同定可能なドメイン(C3–C5)を持っています。COL6A1、COL6A2、COL6A3遺伝子の変異は、ウルリッヒ型先天性筋ジストロフィー(UCMD)およびベスレムミオパチー(BM)の原因であることが知られています。2008年にさらに3つのVI型コラーゲン鎖が報告されました(それぞれCOL6A4、COL6A5、COL6A6にコードされたα4(VI)、α5(VI)、α6(VI)鎖)。
特異性
その他の種は試験していません。
クローン3C4はアルファ-3(VI)鎖の非ヘリックス領域を標的としています。
免疫原
エピトープ:非ヘリックス領域。
精製ヒトコラーゲンVI
アプリケーション
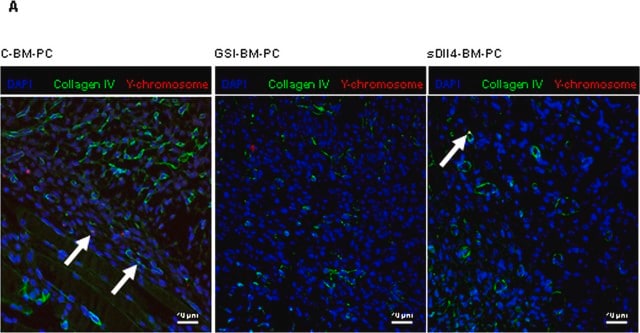
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected intracellular type VI collagen retention by flow cytometry using permeabilized and non-permeabilized fibroblasts isolated from both healthy individuals, as well as Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) and Bethlem myopathy (BM) patients (Kim, J., et al. (2012). Neuromuscul. Disord. 22(2):139-148).
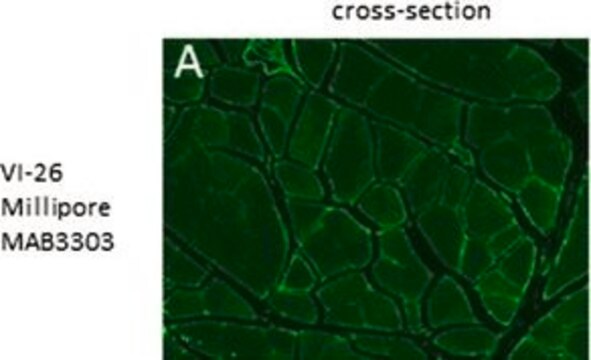
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots detected extracellular type VI collagen immunoreactivity in cultured fibroblasts isolated from Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) and Bethlem myopathy (BM) patients by fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Kim, J., et al. (2012). Neuromuscul. Disord. 22(2):139-148; Allamand, V., et al. (2011). Skelet Muscle. 1:30; Briñas, L., et al. (2010). Ann. Neurol. 68(4):511-520; Jimenez-Mallebrera, C., et al. (2006). Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(9-10):571-582; Tétreault, M., et al. (2004). Brain. 129(Pt 8):2077-2084; Zhang, R.Z., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(46):43557-43564).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected exogenously expressed wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G49A or G301V mutation in SaOS-2 transfectants by fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
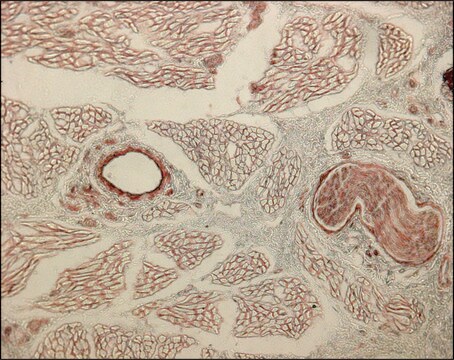
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots immunostained extracellular type VI collagen fibrils in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells and primary foreskin fibroblasts cultures (Bruns, R.R., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 103(2):393-404; Engvall, E., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 102(3):703-710).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected human type VI collagen immunoreactivity in frozen muscle tissue sections from mice grafted with human synovial stem cells (hSSCs) by fluorescent immunohistochemistry (Meng, J., et al. (2010). Neuromuscul. Disord. 20(1):6-15).
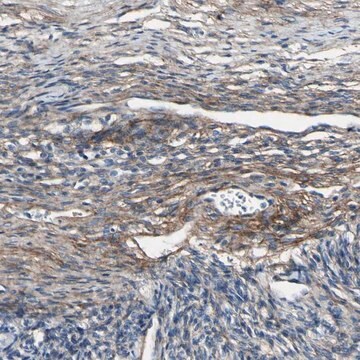
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: Representative lots detected type VI collagen immunoreactivity in muscle and skin samples from congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) and Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) patients by fluorescent immunohistochemistry using frozen tissue sections (Peat, R.A., et al. (2008). Neurology. 71(5):312-321; Jimenez-Mallebrera, C., et al. (2006). Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(9-10):571-582).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot co-immunoprecipitated type VI collagen α1(VI) and α2(VI) chains with wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G16S or G49A mutation. Impaired α1(VI) and α2(VI) co-IP was observed with α3(VI) G301V mutant (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated type VI collagen alpha chains from Triton X-100 extracts of MRC-5 human lung fibroblasts (Engvall, E., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 102(3):703-710).
Electron Microscopy Analysis: A representative lot detected reduced extracellular type VI collagen immunoreactivity in cultured fibroblasts isolated from an Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) patient (Zhang, R.Z., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(46):43557-43564).
Electron Microscopy Analysis: A representative lot immunostained extracellular filaments and fibrils by binding to the band (non-helical) region of the type VI collagen fibrils using cultured human foreskin fibroblasts (Bruns, R.R., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 103(2):393-404).
Dot Blot Analysis: A representative lot detected exogenously expressed wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G49A or G301V mutation in the medium of cultured SaOS-2 transfectants (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots detected extracellular type VI collagen immunoreactivity in cultured fibroblasts isolated from Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) and Bethlem myopathy (BM) patients by fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Kim, J., et al. (2012). Neuromuscul. Disord. 22(2):139-148; Allamand, V., et al. (2011). Skelet Muscle. 1:30; Briñas, L., et al. (2010). Ann. Neurol. 68(4):511-520; Jimenez-Mallebrera, C., et al. (2006). Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(9-10):571-582; Tétreault, M., et al. (2004). Brain. 129(Pt 8):2077-2084; Zhang, R.Z., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(46):43557-43564).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected exogenously expressed wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G49A or G301V mutation in SaOS-2 transfectants by fluorescent immunocytochemistry (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots immunostained extracellular type VI collagen fibrils in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells and primary foreskin fibroblasts cultures (Bruns, R.R., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 103(2):393-404; Engvall, E., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 102(3):703-710).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected human type VI collagen immunoreactivity in frozen muscle tissue sections from mice grafted with human synovial stem cells (hSSCs) by fluorescent immunohistochemistry (Meng, J., et al. (2010). Neuromuscul. Disord. 20(1):6-15).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: Representative lots detected type VI collagen immunoreactivity in muscle and skin samples from congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) and Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) patients by fluorescent immunohistochemistry using frozen tissue sections (Peat, R.A., et al. (2008). Neurology. 71(5):312-321; Jimenez-Mallebrera, C., et al. (2006). Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(9-10):571-582).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot co-immunoprecipitated type VI collagen α1(VI) and α2(VI) chains with wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G16S or G49A mutation. Impaired α1(VI) and α2(VI) co-IP was observed with α3(VI) G301V mutant (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated type VI collagen alpha chains from Triton X-100 extracts of MRC-5 human lung fibroblasts (Engvall, E., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 102(3):703-710).
Electron Microscopy Analysis: A representative lot detected reduced extracellular type VI collagen immunoreactivity in cultured fibroblasts isolated from an Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) patient (Zhang, R.Z., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(46):43557-43564).
Electron Microscopy Analysis: A representative lot immunostained extracellular filaments and fibrils by binding to the band (non-helical) region of the type VI collagen fibrils using cultured human foreskin fibroblasts (Bruns, R.R., et al. (1986). J. Cell Biol. 103(2):393-404).
Dot Blot Analysis: A representative lot detected exogenously expressed wild-type α3(VI) chain, as well as α3(VI) chain with G49A or G301V mutation in the medium of cultured SaOS-2 transfectants (Lamandé, S.R., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(3):1949-1956).
抗VI型コラーゲン抗体であるクローン3C4は、コラーゲンVIアルファ-3鎖の検出において、ドットブロット、電子顕微鏡、フローサイトメトリー、免疫蛍光, 免疫組織染色(パラフィン)、および免疫沈降での使用が検証されています。
研究カテゴリー
細胞構造
細胞構造
研究サブカテゴリー
ECMタンパク質
ECMタンパク質
ターゲットの説明
343.7/321.4/113.2/278.2/134.7 kDa(アイソフォーム1/2/3/4/5プロフォーム)および340.8/318.5/110.4/275.3/131.8 kDa(アイソフォーム1/2/3/4/5成熟フォーム) を算出
物理的形状
未精製。
液体
保管および安定性
-20°Cで凍結保存してください。凍結融解を繰り返さないでください。
法的情報
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
免責事項
メルクのカタログまたは製品に添付されたメルクのその他の文書に記載されていない場合、メルクの製品は研究用途のみを目的としているため、他のいかなる目的にも使用することはできません。このような目的としては、未承認の商業用途、in vitroの診断用途、ex vivoあるいはin vivoの治療用途、またはヒトあるいは動物へのあらゆる種類の消費あるいは適用などがありますが、これらに限定されません。
適切な製品が見つかりませんか。
製品選択ツール.をお試しください
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
MAB1944:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
Adele D'Amico et al.
European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society, 21(6), 873-883 (2017-08-02)
Collagen VI-related disorders (COL6-RD) are a group of heterogenous muscular diseases due to mutations in the COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3 genes, encoding for collagen VI, a critical component of the extracellular matrix. Ullrich congenital muscle disorder and Bethlem myopathy represent
Jong Hee Chae et al.
Journal of medical genetics, 52(3), 208-216 (2015-01-31)
Neuromuscular disorders are a clinically, pathologically, and genetically heterogeneous group. Even for the experienced clinician, an accurate diagnosis is often challenging due to the complexity of these disorders. Here, we investigated the utility of next generation sequencing (NGS) in early
Identification of a deep intronic mutation in the COL6A2 gene by a novel custom oligonucleotide CGH array designed to explore allelic and genetic heterogeneity in collagen VI-related myopathies.
Bovolenta, M; Neri, M; Martoni, E; Urciuolo, A; Sabatelli, P; Fabris, M; Grumati et al.
BMC Medical Genetics null
Arístides López-Márquez et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 23(8) (2022-04-24)
Collagen VI-related disorders are the second most common congenital muscular dystrophies for which no treatments are presently available. They are mostly caused by dominant-negative pathogenic variants in the genes encoding α chains of collagen VI, a heteromeric network forming collagen;
Sara Aguti et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 2176, 221-230 (2020-09-01)
Allele-specific gene silencing by antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) or small interference RNA (siRNA) has been used as a therapeutic approach for conditions caused by dominant gain-of-function mutations. We here present an antisense approach using gapmer ASO to diminish the dominant-negative effect
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)