추천 제품
생물학적 소스
Bacillus sp. (Bacillus cereus)
Quality Level
설명
Merck USA index - 14, 7093
양식
lyophilized
포장
vial of ≥50 units β-lactamase II
vial of ≥500 units β-lactamase I
제조업체/상표
Calbiochem®
저장 조건
OK to freeze
solubility
sterile distilled water: soluble
배송 상태
ambient
저장 온도
−20°C
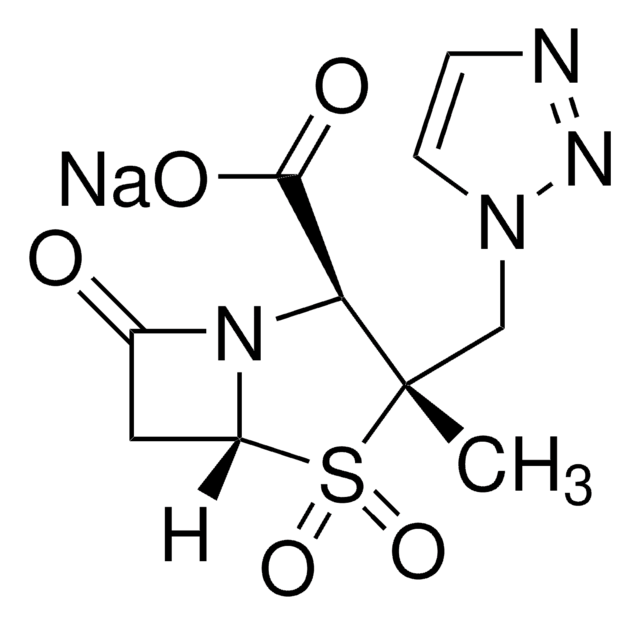
일반 설명
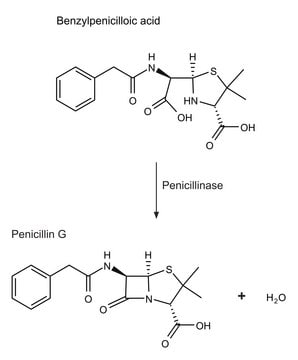
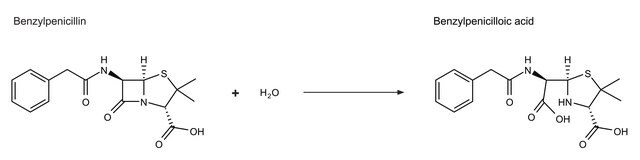
β-Lactamase produced by bacteria shares sequence homology to penicillin-binding proteins. This enzyme is found in Gram-negative bacteria. β-Lactamases have four molecular classes, named A, B, C, and D. A, C, and D form an acyl-enzyme via active site serine residue. Class B β-lactamases are metalloenzymes, which have a zinc ion at their active site for β-lactam hydrolysis.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
β-Lactamase hydrolyzes β-lactum antibiotics and is the chief cause of resistance to β-lactam antibiotics development by bacteria. Mutations in the β-lactamases are associated with extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs).
경고
Toxicity: Harmful (C)
단위 정의
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme that will hydrolyze 1.0 µmol benzyl penicillin and 1.0 µmol of cephalosporin C, respectively, per min at 25°C.
재구성
Following reconstitution, store in the refrigerator (4°C). Stock solutions are stable for up to 1 month at 4°C.
법적 정보
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
이미 열람한 고객
Karen Bush et al.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 54(3), 969-976 (2009-12-10)
Two classification schemes for beta-lactamases are currently in use. The molecular classification is based on the amino acid sequence and divides beta-lactamases into class A, C, and D enzymes which utilize serine for beta-lactam hydrolysis and class B metalloenzymes which
Sibhghatulla Shaikh et al.
Saudi journal of biological sciences, 22(1), 90-101 (2015-01-07)
Antibiotic resistance is a problem of deep scientific concern both in hospital and community settings. Rapid detection in clinical laboratories is essential for the judicious recognition of antimicrobial resistant organisms. Production of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) is a significant resistance-mechanism that
Karen Bush
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 62(10) (2018-08-01)
β-Lactamases, the major resistance determinant for β-lactam antibiotics in Gram-negative bacteria, are ancient enzymes whose origins can be traced back millions of years ago. These well-studied enzymes, currently numbering almost 2,800 unique proteins, initially emerged from environmental sources, most likely
P A Bradford
Clinical microbiology reviews, 14(4), 933-951 (2001-10-05)
Beta-lactamases continue to be the leading cause of resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics among gram-negative bacteria. In recent years there has been an increased incidence and prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), enzymes that hydrolyze and cause resistance to oxyimino-cephalosporins and aztreonam.
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.