추천 제품
형태
liquid
Quality Level
특이 활성도
20.0-60.0 ΔA405/h-μg protein (thiopeptide hydrolysis assay)
미포함
preservative
제조업체/상표
Calbiochem®
저장 조건
OK to freeze
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
배송 상태
wet ice
저장 온도
−70°C
일반 설명
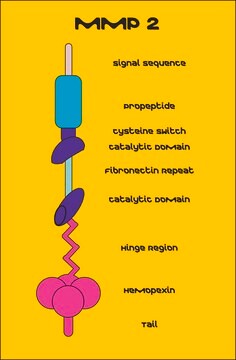
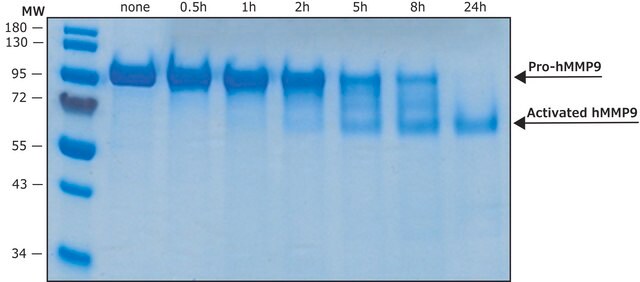
Recombinant, human MMP-9 with a truncated C-terminal hemopexin domain expressed as proenzyme that is activated by APMA. AMPA is removed through a Biogel-P6 column and active MMP-9 is purified.
Recombinant, human MMP-9 with a truncated C-terminal hemopexin domain expressed as proenzyme that is activated by APMA. AMPA is removed through a Biogel-P6 column and active MMP-9 is purified. The substrate specificity for MMP-9 is collagen (types IV, V, VII, and X), elastin, and gelatin (type I). Useful for immunoblotting, substrate cleavage assay, and zymography.
Matrix metalloproteinases are members of a unique family of proteolytic enzymes that have a zinc ion at their active sites and can degrade collagens, elastin and other components of the extracellular matrix (ECM). These enzymes are present in normal healthy individuals and have been shown to have an important role in processes such as wound healing, pregnancy, and bone resorption. However, overexpression and activation of MMPs have been linked with a range of pathological processes and disease states involved in the breakdown and remodeling of the ECM. Such diseases include tumor invasion and metastasis, rheumatoid arthritis, periodontal disease, and vascular processes such as angiogenesis, intimal hyperplasia, atherosclerosis and aneurysms. Recently, MMPs have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Natural inhibitors of MMPs, tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs) exist and synthetic inhibitors have been developed which offer hope of new treatment options for these diseases. Regulation of MMP activity can occur at the level of gene expression, including transcription and translation, level of activation, or at the level of inhibition by TIMPs. Thus, perturbations at any of these points can theoretically lead to alterations in ECM turnover. Expression is under tight control by pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and/or growth factors and, once produced the enzymes are usually secreted as inactive zymograms. Upon activation (removal of the inhibitory propeptide region of the molecules) MMPs are subject to control by locally produced TIMPs. All MMPs can be activated in vitro with organomercurial compounds (e.g., 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate), but the agents responsible for the physiological activation of all MMPs have not been clearly defined. Numerous studies indicate that members of the MMP family have the ability to activate one another. The activation of the MMPs in vivo is likely to be a critical step in terms of their biological behavior, because it is this activation that will tip the balance in favor of ECM degradation. The hallmark of diseases involving MMPs appear to be stoichiometric imbalance between active MMPs and TIMPs, leading to excessive tissue disruption and often degradation. Determination of the mechanisms that control this imbalance may open up some important therapeutic options of specific enzyme inhibitors.
Matrix metalloproteinases are members of a unique family of proteolytic enzymes that have a zinc ion at their active sites and can degrade collagens, elastin and other components of the extracellular matrix (ECM). These enzymes are present in normal healthy individuals and have been shown to have an important role in processes such as wound healing, pregnancy, and bone resorption. However, overexpression and activation of MMPs have been linked with a range of pathological processes and disease states involved in the breakdown and remodeling of the ECM. Such diseases include tumor invasion and metastasis, rheumatoid arthritis, periodontal disease, and vascular processes such as angiogenesis, intimal hyperplasia, atherosclerosis and aneurysms. Recently, MMPs have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Natural inhibitors of MMPs, tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs) exist and synthetic inhibitors have been developed which offer hope of new treatment options for these diseases. Regulation of MMP activity can occur at the level of gene expression, including transcription and translation, level of activation, or at the level of inhibition by TIMPs. Thus, perturbations at any of these points can theoretically lead to alterations in ECM turnover. Expression is under tight control by pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and/or growth factors and, once produced the enzymes are usually secreted as inactive zymograms. Upon activation (removal of the inhibitory propeptide region of the molecules) MMPs are subject to control by locally produced TIMPs. All MMPs can be activated in vitro with organomercurial compounds (e.g., 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate), but the agents responsible for the physiological activation of all MMPs have not been clearly defined. Numerous studies indicate that members of the MMP family have the ability to activate one another. The activation of the MMPs in vivo is likely to be a critical step in terms of their biological behavior, because it is this activation that will tip the balance in favor of ECM degradation. The hallmark of diseases involving MMPs appear to be stoichiometric imbalance between active MMPs and TIMPs, leading to excessive tissue disruption and often degradation. Determination of the mechanisms that control this imbalance may open up some important therapeutic options of specific enzyme inhibitors.
애플리케이션
Immunoblotting (1μg protein/lane)
Zymography (0.1 μg protein/lane, see application references)
Zymography (0.1 μg protein/lane, see application references)
포장
Please refer to vial label for lot-specific concentration.
경고
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
물리적 형태
In 50 mM Hepes, 10 mM CaCl₂, 20% glycerol, 0.005% BRIJ® 35 Detergent, pH 7.5.
재구성
Following initial thaw, aliquot and freeze (-70°C).
기타 정보
Parsons, S.L., et al. 1997. Br. J. Surg.84, 160.
Backstrom, J.R., et al. 1996. J. Neuro.16, 7910.
Lim, G.P., et al. 1996. J Neurochem.67.
Xia, T., et al. 1996. Biochim. Biophys.1293, 259.
Sang, Q.X., et al. 1995. Biochim. Biophys.1251, 99.
Zempo, N., et al. 1994. J. Vasc. Surg.20, 209.
Birkedal-Hansen, H. 1993. J. Periodontol64, 474.
Stetler-Stevenson, W.G., et al. 1993. FASEB J.7, 1434.
Jeffrey, J.J. 1991. Semin. Perinatol.15, 118.
Liotta, L.A., et al. 1991. Cell64, 327.
Harris, E. 1990. N. Engl. J. Med.322, 1277.
Backstrom, J.R., et al. 1996. J. Neuro.16, 7910.
Lim, G.P., et al. 1996. J Neurochem.67.
Xia, T., et al. 1996. Biochim. Biophys.1293, 259.
Sang, Q.X., et al. 1995. Biochim. Biophys.1251, 99.
Zempo, N., et al. 1994. J. Vasc. Surg.20, 209.
Birkedal-Hansen, H. 1993. J. Periodontol64, 474.
Stetler-Stevenson, W.G., et al. 1993. FASEB J.7, 1434.
Jeffrey, J.J. 1991. Semin. Perinatol.15, 118.
Liotta, L.A., et al. 1991. Cell64, 327.
Harris, E. 1990. N. Engl. J. Med.322, 1277.
The substrate specificity for MMP-9 is collagen (types IV, V, VII, and X), elastin, and gelatin (type I).
법적 정보
Brij is a registered trademark of Croda International PLC
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
이미 열람한 고객
Maciej J Stawikowski et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 1579, 137-183 (2017-03-17)
A continuous assay method, such as the one that utilizes an increase in fluorescence upon hydrolysis, allows for rapid and convenient kinetic evaluation of proteases. To better understand MMP behaviors toward native substrates, a variety of fluorescence resonance energy transfer
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.