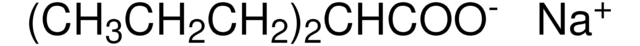A1757
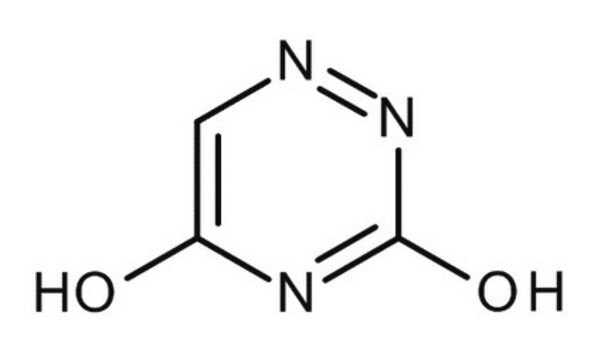
6-Azauracil
≥98%
동의어(들):
6-AU, 1,2,4-Triazine-3,5(2H,4H)-dione, 3,5-Dihydroxy-1,2,4-triazine, 6-Aza-2,4-dihydroxypyrimidine
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
모든 사진(2)
About This Item
실험식(Hill 표기법):
C3H3N3O2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
113.07
Beilstein:
116472
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC 코드:
41106305
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.51
추천 제품
애플리케이션
6-Azauracil has been used as a transcriptional inhibitor to study its effects on the deletion of termination and polyadenylation protein (Tpa1) and Mag1 on cell viability. It has also been used as an orotidine-5′-monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPdecase) inhibitor in minimal media for determining the OMPdecase activity.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
6-Azauracil (6-AU) is a pyrimidine analog of uracil and exhibits antitumor activity. It inhibits the growth of various microorganisms by depleting intracellular guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP) nucleotide pools.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
이미 열람한 고객
Hai-Ning Du et al.
Genes & development, 22(20), 2786-2798 (2008-10-17)
Set2-mediated H3 K36 methylation is an important histone modification on chromatin during transcription elongation. Although Set2 associates with the phosphorylated C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII), the mechanism of Set2 binding to chromatin and subsequent exertion of its
Clinical studies of 6-azauracil
Shnider BI, et al.
Cancer Research, 20(1), 28-33 (1960)
Kazuko Matsubara et al.
Genes to cells : devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms, 12(1), 13-33 (2007-01-11)
The core histones are essential components of the nucleosome that act as global negative regulators of DNA-mediated reactions including transcription, DNA replication and DNA repair. Modified residues in the N-terminal tails are well characterized in transcription, but not in DNA
Peter L Freddolino et al.
eLife, 7 (2018-04-06)
Cells adapt to familiar changes in their environment by activating predefined regulatory programs that establish adaptive gene expression states. These hard-wired pathways, however, may be inadequate for adaptation to environments never encountered before. Here, we reveal evidence for an alternative
Rahul V Nene et al.
PLoS genetics, 14(1), e1007170-e1007170 (2018-01-11)
Defects in the genes encoding the Paf1 complex can cause increased genome instability. Loss of Paf1, Cdc73, and Ctr9, but not Rtf1 or Leo1, caused increased accumulation of gross chromosomal rearrangements (GCRs). Combining the cdc73Δ mutation with individual deletions of
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.