추천 제품
생물학적 소스
rabbit
Quality Level
결합
unconjugated
항체 형태
affinity isolated antibody
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
polyclonal
양식
lyophilized powder
종 반응성
mouse, rat
기술
immunocytochemistry: 1:30-1:150
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot (chemiluminescent): 1:100-1:200
UniProt 수납 번호
저장 온도
−20°C
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
유전자 정보
human ... CACNA1D(776)
mouse ... Cacna1d(12289)
rat ... Cacna1d(29716)
면역원
synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids 859-875 of rat α1D (Accession P27732). This epitope is highly conserved in human and hamster.
애플리케이션
Anti-Calcium Channel (α1D Subunit) (L-type of Voltage-gated Ca2+ Channel) antibody produced in rabbit is suitable for the following applications:
- immunocytochemistry at a dilution of 1:30-1:150
- immunoprecipitation
- western blot (chemiluminescent) at a dilution of 1:100-1:200
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Cav1.3 also known as the calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, α1D subunit (CACNA1D), is a human gene. It responds more sensitively to depolarization than those of Cav1.2 or Cav3.1. Cav1.3 is required for proper hearing as well as sinoatrial node and brain function. It undergoes extensive alternative splicing. Alternative splicing in the C terminus and drastically modifies gating properties of the channel. The L-type calcium channel Cav1.3 is important in human glucose-induced insulin secretion and common variants in CACNA1D may contribute to type 2 diabetes.
물리적 형태
Lyophilized from phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% BSA and 0.05% sodium azide
면책조항
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
Hua Huang et al.
Molecular pharmacology, 84(4), 643-653 (2013-08-09)
The transcripts of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels (CaV) 1.3 undergo extensive alternative splicing. Alternative splicing, particularly in the C terminus, drastically modifies gating properties of the channel. However, little is known about whether alternative splicing could modulate the pharmacologic properties
Jan Salomonsen et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(24), 8668-8673 (2005-06-09)
CD1 molecules play an important role in the immune system, presenting lipid-containing antigens to T and NKT cells. CD1 genes have long been thought to be as ancient as MHC class I and II genes, based on various arguments, but
T M Reinbothe et al.
Diabetologia, 56(2), 340-349 (2012-12-12)
Voltage-gated calcium channels of the L-type have been shown to be essential for rodent pancreatic beta cell function, but data about their presence and regulation in humans are incomplete. We therefore sought to elucidate which L-type channel isoform is functionally
Andreas Lieb et al.
Biophysical journal, 106(7), 1467-1475 (2014-04-08)
Activity of voltage-gated Cav1.3 L-type Ca(2+) channels is required for proper hearing as well as sinoatrial node and brain function. This critically depends on their negative activation voltage range, which is further fine-tuned by alternative splicing. Shorter variants miss a
Allison Sargoy et al.
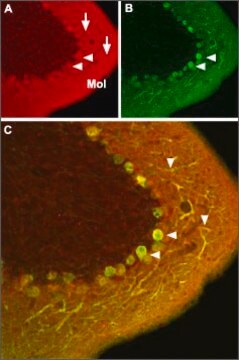
PloS one, 9(1), e84507-e84507 (2014-01-15)
Aberrant calcium regulation has been implicated as a causative factor in the degeneration of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) in numerous injury models of optic neuropathy. Since calcium has dual roles in maintaining homeostasis and triggering apoptotic pathways in healthy and
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.