추천 제품
생화학적/생리학적 작용
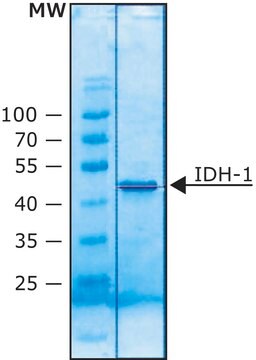
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) plays a major role in the Krebs cycle by catalyzing the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate.[1] The oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate generates α-ketoglutarate and NADPH. NADPH produced is essential for the production of fatty acids and cholesterol.[2] This NADP-dependent molecules serves as homodimers.[3]
품질
Crude
단위 정의
One unit will convert 1.0 μmole of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate per min at pH 7.4 at 37°C.
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
예방조치 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
이미 열람한 고객
Chapter One - Mechanisms of Epigenetic Regulation of Leukemia Onset and Progression
Ntziachristos P, et al.
Advances in Immunology, 117, 1-38 (2013)
The Molecular Pathogenesis of Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, 21-31 (2016)
Molecular Testing for Glioblastoma
Diagnostic Molecular Pathology, 339-347 (2017)
Rithvik Vinekar et al.
BMC bioinformatics, 13 Suppl 17, S2-S2 (2013-01-11)
Isocitrate Dehydrogenases (IDHs) are important enzymes present in all living cells. Three subfamilies of functionally dimeric IDHs (subfamilies I, II, III) are known. Subfamily I are well-studied bacterial IDHs, like that of Escherischia coli. Subfamily II has predominantly eukaryotic members
Jay P Patel et al.
Hematology. American Society of Hematology. Education Program, 2012, 28-34 (2012-12-13)
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common acute leukemia diagnosed in adults, and the majority of patients with AML die from relapsed disease. Although many studies over the past 4 decades have identified disease alleles in AML, recent genome-wide
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.