151777
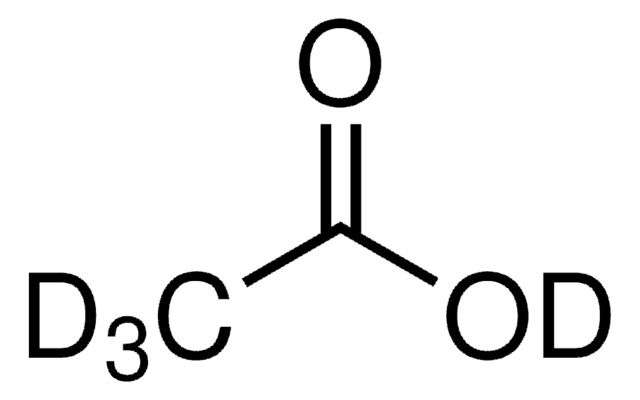
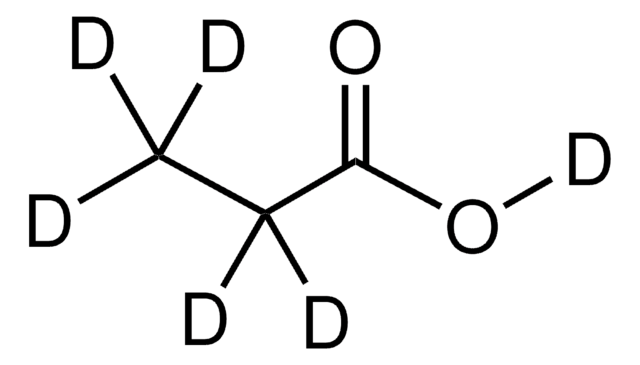
Acetic acid-d
99 atom % D
Synonym(s):
mono-Deuteroacetic acid, Acetic (acid-d), Monodeuteroacetic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH3COOD
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
61.06
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
1739249
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12142201
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.21
Recommended Products
vapor density
2.07 (vs air)
Quality Level
vapor pressure
11.4 mmHg
isotopic purity
99 atom % D
assay
99% (CP)
form
liquid
expl. lim.
4-19.9 % (lit.)
technique(s)
NMR: suitable
impurities
≤0.50% water
water
bp
116-117 °C (lit.)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Acetic acid-d (Monodeuteroacetic acid) is the monodeuterated form of acetic acid, in which the hydrogen atom of hydroxyl group has been replaced by deuterium (D). Infrared spectral studies of its vapors at 150°C in the range of 2-25μ have been reported.
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Corr. 1A
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
104.0 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
40 °C - closed cup
ppe
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Vennela Mullangi et al.
Biochemistry, 51(36), 7202-7208 (2012-08-21)
We report a method for expressing the solvent accessibility of histidine imidazole groups in proteins. The method is based on measuring the rate of the hydrogen exchange (HX) reaction of the imidazole C(ε1)-hydrogen. The rate profile of the HX reaction
Infrared Investigation of Acetic Acid and Acetic Acid-d Vapors and a Vibrational Assignment for the Monomeric Acids.
Wilmshurst JK.
J. Chem. Phys. , 25(6), 1171-1173 (1956)
Li-Min Peng et al.
PeerJ, 4, e1519-e1519 (2016-01-21)
According to myosatellite cell lines (MSCs) established in vitro from diploid and triploid flounder, we compared the characters of growth and differentiation of their MSCs. The results would be useful for learning the muscle development mechanism in teleosts. The skeletal
B R Miller et al.
Neuroscience, 153(1), 329-337 (2008-03-21)
The striatum, which processes cortical information for behavioral output, is a key target of Huntington's disease (HD), an autosomal dominant condition characterized by cognitive decline and progressive loss of motor control. Increasing evidence implicates deficient glutamate uptake caused by a
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service