25890
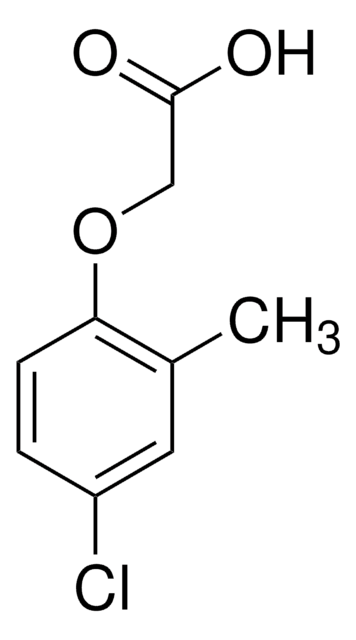
4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
≥98.0% (T)
Synonym(s):
4-CPA
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C8H7ClO3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
186.59
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
1211804
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
assay
≥98.0% (T)
form
powder
functional group
carboxylic acid
chloro
SMILES string
OC(=O)COc1ccc(Cl)cc1
InChI
1S/C8H7ClO3/c9-6-1-3-7(4-2-6)12-5-8(10)11/h1-4H,5H2,(H,10,11)
InChI key
SODPIMGUZLOIPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid is a herbicide. Degradation of 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid in aqueous medium by advanced electrochemical oxidation processes, using an undivided cell containing a Pt anode has been reported.
Application
- Innovative adsorbents for chemical analysis: The application of three-dimensional material CZIF-8/CS-MS was explored as adsorbents for the determination of plant growth regulators including 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid in traditional Chinese medicine, improving the precision and efficiency of chemical residue analysis (Zhang et al., 2024).
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Shenghuai Hou et al.
Food chemistry, 321, 126702-126702 (2020-04-03)
A new amino-modified Scholl-coupling mesoporous polymer (NH2@SMPA)-online solid-phase extraction method, coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (online SPE-HPLC) was established for the analysis of six plant growth regulators (PGRs) in bean sprouts. NH2@SMPA was synthesized by acid-catalyzed deacetylation of acetylamino-Scholl-coupling mesoporous
Sze Chieh Tan et al.
Talanta, 216, 120962-120962 (2020-05-28)
Two miniaturized sample preparation techniques, ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction (USAEME) and micro-solid-phase extraction (μ-SPE) have been integrated for the pre-concentration of four polar chlorophenoxy acid (CPA) herbicides from environmental aqueous samples. An metal-organic framework, MIL-101(Cr), characterized by its high porosity and
Song Zhu et al.
Food science and biotechnology, 29(11), 1587-1595 (2020-10-23)
Determination of phytohormones have attracted increasing attentions in food safety field. In this study, an efficient and quantitative method was developed which can simultaneously determinate thirteen phytohormones in fruits and vegetables using solid phase extraction (SPE) combined with high performance
Sze Chieh Tan et al.
Mikrochimica acta, 188(2), 30-30 (2021-01-09)
A novel solvent-loaded dispersive solid-phase extraction (SL-DSPE) method integrated with liquid-phase microextraction (LPME) has been developed by the direct loading of solvent into the pores of a metal-organic framework (MOF), MIL-101(Cr)-NH2. Despite numerous advantages of MOFs, they are usually highly hydrophobic
Sonia Traverso et al.
The Journal of general physiology, 122(3), 295-306 (2003-08-13)
Opening of CLC chloride channels is coupled to the translocation of the permeant anion. From the recent structure determination of bacterial CLC proteins in the closed and open configuration, a glutamate residue was hypothesized to form part of the Cl--sensitive
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service