302341
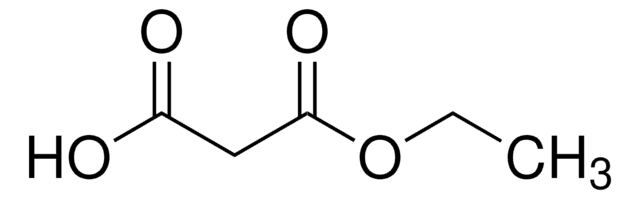
Acetoxyacetic acid
99%
Synonym(s):
α-Acetoxyacetic acid, (Acetyloxy)acetic acid, 2-(Acetyloxy)acetic acid, 2-Hydroxyacetic acid acetate, Acetylglycolic acid, O-Acetylglycolic acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
99%
bp
141-142 °C/12 mmHg (lit.)
mp
67-69 °C (lit.)
functional group
carboxylic acid
ester
SMILES string
CC(=O)OCC(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H6O4/c1-3(5)8-2-4(6)7/h2H2,1H3,(H,6,7)
InChI key
MLXDUYUQINCFFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Application
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service