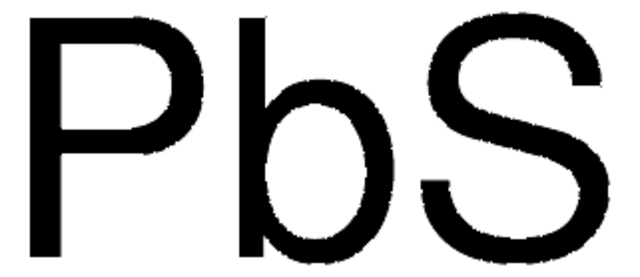935085
Infrared PbS quantum dots
λmax, 1650 nm, 100 mg/mL in toluene
Synonym(s):
Fluorescent nanocrystals, INFIQ® quantum dots, Lead based core type QDs
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
>6 peak/valley ratio
Quality Level
form
liquid
concentration
100 mg/mL in toluene
100 mg/mL
particle size
<15 nm (Nanoparticle)
λmax
<100 nm (FWHM)
1650 nm
storage temp.
2-8°C
InChI
1S/Pb.S
InChI key
XCAUINMIESBTBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Legal Information
Related product
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Asp. Tox. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Repr. 1A - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 2 - STOT RE 2 Inhalation - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Central nervous system
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
39.2 °F
flash_point_c
4 °C
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service