W288608
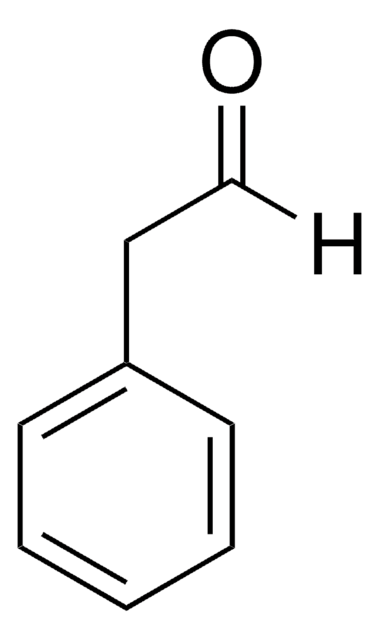
2-Phenylpropionaldehyde
≥95%, FCC, FG
Synonym(s):
2-Phenylpropanal, Hydratropaldehyde
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic
Quality Level
grade
FG
Halal
Kosher
agency
meets purity specifications of JECFA
reg. compliance
EU Regulation 1334/2008 & 178/2002
FCC
FDA 21 CFR 172.515
assay
≥95%
refractive index
n20/D 1.517 (lit.)
bp
92-94 °C/12 mmHg (lit.)
density
1.002 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
application(s)
flavors and fragrances
documentation
see Safety & Documentation for available documents
food allergen
no known allergens
organoleptic
fresh; green; floral
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[H]C(=O)C(C)c1ccccc1
InChI
1S/C9H10O/c1-8(7-10)9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h2-8H,1H3
InChI key
IQVAERDLDAZARL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Cytotoxicity, early safety screening, and antimicrobial potential of minor oxime constituents of essential oils and aromatic extracts.: Explores the safety and effectiveness of 2-Phenylpropionaldehyde among other compounds in essential oils, highlighting its potential antimicrobial properties and implications for food safety and preservation (Strub DJ et al., 2022).
- Spectroscopic Evidence for a Cobalt-Bound Peroxyhemiacetal Intermediate.: This study provides spectroscopic evidence of a cobalt-bound intermediate in reactions involving 2-Phenylpropionaldehyde, advancing our knowledge of chemical reaction mechanisms and catalysis (Cho J et al., 2021).
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
174.2 °F
flash_point_c
79 °C
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service