11202375001
Roche
DOTAP Liposomal Transfection Reagent
>99% (TLC), liquid, suitable for transfection
Synonym(s):
DOTAP methosulfate, liposomal transfection reagent, dotap, transfection reagent, dotap, N-(2,3-Dioleoyloxy-1-propyl)trimethylammonium methyl sulfate, Transfection reagent
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
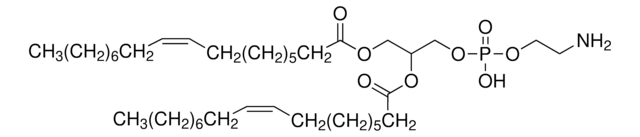
N-[1-(2,3-Dioleoyloxy)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethylammonium methyl-sulfate
Quality Level
assay
>99% (TLC)
form
liquid
packaging
pkg of 5 × 400 μL (10 U/μl)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
technique(s)
transfection: suitable
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[H]C(C[N+](C)(C)C)(OC(CCCCCCC/C=C\CCCCCCCC)=O)COC(CCCCCCC/C=C\CCCCCCCC)=O.O=S([O-])(OC)=O
InChI
1S/C42H80NO4.CH4O4S/c1-6-8-10-12-14-16-18-20-22-24-26-28-30-32-34-36-41(44)46-39-40(38-43(3,4)5)47-42(45)37-35-33-31-29-27-25-23-21-19-17-15-13-11-9-7-2;1-5-6(2,3)4/h20-23,40H,6-19,24-39H2,1-5H3;1H3,(H,2,3,4)/q+1;/p-1/b22-20-,23-21-;
InChI key
RSMRWWHFJMENJH-LQDDAWAPSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Features and Benefits
- Easy to use: The lipid dispersion is simply mixed with the DNA solution, then applied directly to the cells
- Highly effective: 5 to 100-fold more effective than the calcium phosphate or DEAE-dextran method
- Gentle: No cytotoxic effects
- Flexible: Equally effective in the presence or absence of serum. Effective on a wide range of species (e.g., insect cells, mammalian cells) and a variety of different cell types. Can be used for either transient or stable transfection procedures.
- Aqueous dispersion (liposomes) in MBS (MES-buffered saline, pH 6.2) (bottled under argon), 1mg/ml, sterile-filtered.
Preparation Note
The optimal working concentration is dependent on several parameters, including the cell line being used, concentration and type of nucleic acid (DNA, RNA), and incubation time. It is important to optimize the transfection conditions for the individual cell type studied.
Cytotoxicity: Not cytotoxic up to a concentration of 100μg/ml (PBLs, HeLa cells).
Other Notes
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
nwg
flash_point_f
does not flash
flash_point_c
does not flash
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
This brief webinar provides an overview of what transfection is and the methods that are used to introduce DNA or RNA into eukaryotic cells.
Related Content
Browse our convenient transfection reagent selection guide to match the best reagent for your specific cell line and application needs.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service