11480
Azelaic acid
technical, ~85% (GC)
Synonym(s):
Nonanedioic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
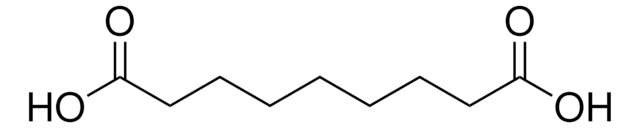
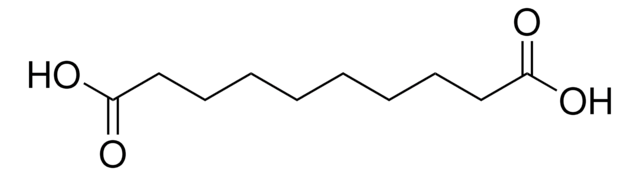
HO2C(CH2)7CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
188.22
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
1101094
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
vapor density
6.5 (vs air)
Quality Level
vapor pressure
<1 mmHg ( 20 °C)
grade
technical
assay
~85% (GC)
bp
286 °C/100 mmHg (lit.)
mp
109-111 °C (lit.)
functional group
carboxylic acid
SMILES string
OC(=O)CCCCCCCC(O)=O
InChI
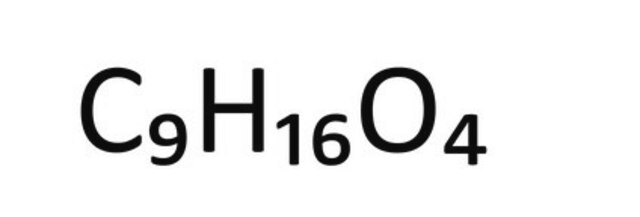
1S/C9H16O4/c10-8(11)6-4-2-1-3-5-7-9(12)13/h1-7H2,(H,10,11)(H,12,13)
InChI key
BDJRBEYXGGNYIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Azelaic acid (Nonanedioic acid) is a naturally occurring saturated, nonphenolic compound isolated from cultures Pityrosporum ovale. It is a therapeutic agent with well-known antibacterial properties.
Application
- A phase 3 randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial of azelaic acid foam 15% in the treatment of papulopustular rosacea: This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of a 15% azelaic acid foam in treating rosacea, demonstrating significant improvements in disease severity (Draelos et al., 2015).
- Comparison of the characteristics of transfersomes and protransfersomes containing azelaic acid: This research compares the properties of transfersome formulations with azelaic acid, highlighting their potential for enhanced delivery in dermatological applications (Rahmi and Pangesti, 2018).
- Enhancing the bioconversion of azelaic acid to its derivatives by response surface methodology: This article discusses optimizing the production of azelaic acid derivatives, which are crucial for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications (Khairudin et al., 2018).
- Azelaic acid: a bio-based building block for biodegradable polymers: The study explores azelaic acid as a sustainable precursor for producing biodegradable polymers, pertinent to material science (Todea et al., 2021).
- Preparation and evaluation of azelaic acid topical microemulsion formulation: in vitro and in vivo study: This research presents a microemulsion formulation of azelaic acid, assessing its stability and skin permeability, critical for topical therapeutic applications (Hung et al., 2021).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Azelaic acid is a potent inhibitor of 5α-reductase activity. It is a reversible competitive inhibitor of thioredoxin reductase in human melanoma cells.
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
410.0 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
210 °C - closed cup
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
K U Schallreuter et al.
Cancer letters, 36(3), 297-305 (1987-09-01)
Azelaic acid has been shown to inhibit thioredoxin reductase (TR) at the surface of guinea pig and human skin, on cultures of human keratinocytes, melanocytes, melanoma cells, murine melanoma cells (Cloudman S91), and on purified enzymes from Escherichia coli, rat
D Stamatiadis et al.
The British journal of dermatology, 119(5), 627-632 (1988-11-01)
The effects of zinc sulphate and azelaic acid on 5 alpha-reductase activity in human skin were studied using an in vitro assay with 1,2[3H]-testosterone as substrate. When added at concentrations of 3 or 9 mmol/l, zinc was a potent inhibitor
Ji Sun Yu et al.
Journal of biomedical science, 17 Suppl 1, S45-S45 (2010-09-11)
Pigmentation in human skin is an important defense mechanism against sunlight or oxidative stress. Despite the protective role of melanin, abnormal hyperpigmentation such as freckles and chloasma sometimes can be serious aesthetic problems. Because of these effects of hyperpigmentation, people
J Brasch et al.
Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland), 186(1), 55-58 (1993-01-01)
Azelaic acid is a therapeutic agent with well-known antibacterial properties, but its antimycotic effect has not yet been investigated systematically. In this study we have used an agar dilution technique to test the inhibitory effect of azelaic acid upon common
Alvin B Coda et al.
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 69(4), 570-577 (2013-07-23)
Excess cathelicidin and kallikrein 5 (KLK5) have been hypothesized to play a role in the pathophysiology of rosacea. We sought to evaluate the effects of azelaic acid (AzA) on these elements of the innate immune system. Gene expression and protease
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service