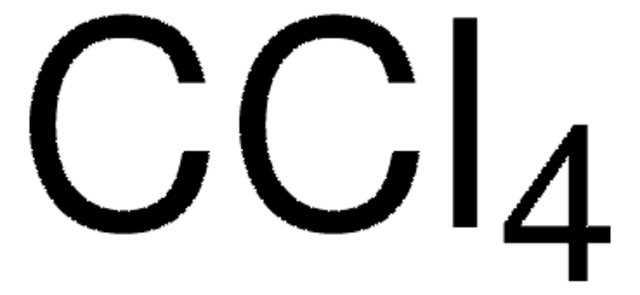319961
Carbon tetrachloride
reagent grade, 99.9%
Synonym(s):
Tetrachloromethane
Select a Size
Select a Size
About This Item
91 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Recommended Products
grade
reagent grade
Quality Level
vapor density
5.32 (vs air)
vapor pressure
143 mmHg ( 30 °C)
91 mmHg ( 20 °C)
assay
99.9%
form
liquid
dilution
(for analytical testing)
refractive index
n20/D 1.460 (lit.)
bp
76-77 °C (lit.)
mp
−23 °C (lit.)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- A precursor to synthesize high-surface-area mesoporous carbon material by a self-templating method in the presence of sodium-potassium alloy (NaK) as a reducing agent.
- A reactant to synthesize 1,2-disubstituted cyclopentanes via Cu-catalyzed ring-closing Kharasch addition reaction with 1,6-dienes.
- A solvent as well as a reactant to prepare diphenyl carbonate from phenol and carbon dioxide in the presence of ZnCl2 as a catalyst.
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Carc. 2 - Ozone 1 - Skin Sens. 1B - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
target_organs
Liver,Kidney
Storage Class
6.1B - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service