G0535
Glycopeptidase A from almonds
buffered aqueous glycerol solution, ≥0.05 unit/mL
Synonym(s):
N-Glycosidase A, N-linked-glycopeptide-(N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminyl)-L-asparagine amidohydrolase, PNGase A
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
conjugate
(N-linked)
Quality Level
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
concentration
≥0.05 unit/mL
storage temp.
−20°C
Related Categories
General description
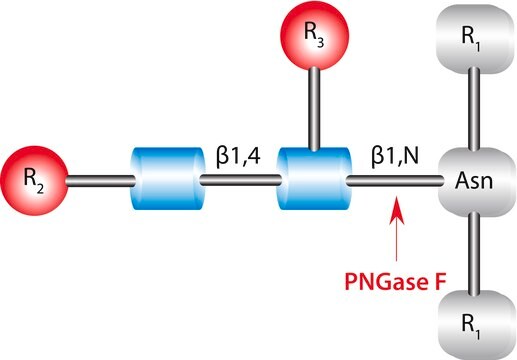
Glycopeptidase found in almonds can be divided into three groups- A, B and C. the optimum pH value and the isoelectric point of glycopeptidase A is 6.0 and 7.7 respectively. It has a preference for glycopeptides with long chains. It is also capable of hydrolyzing intact glycoproteins such as, desialyted human transferrin, ovalbumin etc. These proteins cleave glycoproteins with asialocarbohydrate moieties at their β-aspartyl-glucosylamine linkages.
Application
Glycopeptidase A from almonds is used for deglycosylation. It catalyzes the removal of N-linked oligosaccharide chains and converts Asn residue to Asp.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Hydrolyzes an N4-(acetyl-β-D-glycosaminyl)asparagine in which the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residue may be further glycosylated, yielding a (substituted) N-acetyl-β-D-glucoaminylamine and the peptide containing an aspartic residue.
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of ovalbumin glycopeptide per min at pH 5.0 at 37°C.
Physical form
Solution in 50% glycerol containing 50 mM citrate-phosphate buffer, pH 5.0, and BSA.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
No data available
flash_point_c
No data available
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
T Takahashi et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 657(2), 457-467 (1981-02-13)
The glycopeptidase preparation that has been isolated from almond emulsin and acts on beta-aspartylglycosylamine linkages in glycopeptides was separated into three active fractions by DEAE-cellulose column chromatography. The three discrete species of glycopeptidase (Groups A, B and C) have been
Asparagine-linked oligosaccharides in human placenta and umbilical cord as demonstrated by almond glycopeptidase.
N Takahashi et al.
FEBS letters, 146(1), 139-142 (1982-09-06)
Karen G Welinder et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 284(15), 9764-9769 (2009-02-13)
Proteome data of potato (Solanum tuberosum) tuber juice and of purified potato tuber vacuoles indicated that mature patatins may perhaps lack a C-terminal propeptide. We have confirmed this by complete mass spectrometric sequencing of a number of patatin variants as
R P Miller et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 954(1), 50-57 (1988-04-28)
The beta-subunit of dog kidney (Na+ + K+)-ATPase is a sialoglycoprotein and contains three potential N-glycosylation sites. In this study, the oligosaccharide chains of purified dog kidney beta-subunit were labeled with tritium by oxidation with sodium periodate or galactose oxidase
Zhaohai Zhang et al.
The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 44(8), 1244-1253 (2012-05-15)
Correlations of disease phenotypes with glycosylation changes have been analyzed intensively in tumor biology field. In this study we describe glycomic alterations of multidrug resistance in human leukemia cell lines. Using multiple glycan profiling tools: real-time PCR for quantification of
Articles
Explore strategies for releasing N-linked glycans with PNGase F, PNGase A & native & sequential deglycosylation with endoglycosidases & exoglycosidases.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service