MBD0002
Microbial DNA standard from Proteus mirabilis
Suitable for PCR, sequencing and NGS
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.24
Recommended Products
Quality Level
form
liquid
concentration
10 ng/μL
technique(s)
DNA extraction: suitable
DNA sequencing: suitable
PCR: suitable
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
Related Categories
General description
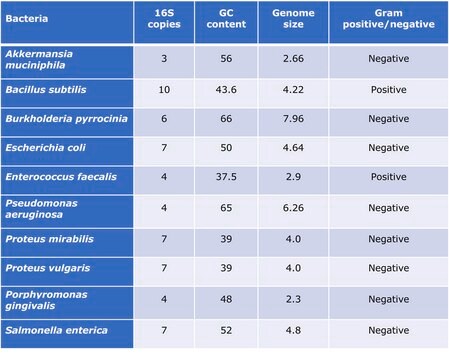
Standardization of sample analysis is currently needed in microbiome genomics research workflow. Lack of standardization can lead to biases and errors in common processes during sample preparation and analysis such as sample amplification, sequencing and bioinformatics analyses.1 Proteus mirabilis genomic DNA microbial standard can serve as standard for benchmarking the performance along the workflow of microbiomics or meta-genomics analyses and as a tool to increase reproducibility and allow comparison of results obtained by different labs.
Proteus mirabilis is a gram negative facultative anaerobic rod-shaped bacterium. Bacteria of the genus Proteus of the family Enterobacteriaceae are opportunistic human pathogens responsible for wound and burn infections as well as skin, eye, ear, nose, throat, urinary tract, and gastrointestinal infections and bacteremias.2 The most common infection involving P. mirabilis occurs when the bacteria, which is a member of the natural intestinal flora, moves to the urethra and urinary bladder causing urinary tract infection. The outer-membrane lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is considered an important virulence factor of Proteus.3 Arabski et al. suggest that the immunological response against P. mirabilis LPS might play a role in rheumatoid arthritis.4 A possible correlation between the abundance of P. mirabilis in the intestine and obesity was suggested recently.5
Read here how to use our standards to ensure data integrity for your microbiome research.
Proteus mirabilis is a gram negative facultative anaerobic rod-shaped bacterium. Bacteria of the genus Proteus of the family Enterobacteriaceae are opportunistic human pathogens responsible for wound and burn infections as well as skin, eye, ear, nose, throat, urinary tract, and gastrointestinal infections and bacteremias.2 The most common infection involving P. mirabilis occurs when the bacteria, which is a member of the natural intestinal flora, moves to the urethra and urinary bladder causing urinary tract infection. The outer-membrane lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is considered an important virulence factor of Proteus.3 Arabski et al. suggest that the immunological response against P. mirabilis LPS might play a role in rheumatoid arthritis.4 A possible correlation between the abundance of P. mirabilis in the intestine and obesity was suggested recently.5
Read here how to use our standards to ensure data integrity for your microbiome research.
Application
Suitable for Quantitative standard for PCR, Sequencing and NGS
Features and Benefits
- Individual microbial standard for microbiomics and meta-genomics workflow
- Suitable standard for PCR, sequencing and NGS
- Improve Bioinformatics analyses
- Increases reproducibility
- Compare results lab to lab
Physical form
Liquid -The genomic DNA is provided at ≥10 ng/μl concentration in TE buffer pH 8.0
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Michal Arabski et al.
Clinical biochemistry, 45(16-17), 1374-1382 (2012-07-04)
Proteus mirabilis strains are human pathogens responsible for urinary tract infections, which may also be involved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We determined whether the binding site of anti-LPS antibodies on the O-polysaccharide part of P. mirabilis LPS correlates with the
A Rózalski et al.
Microbiology and molecular biology reviews : MMBR, 61(1), 65-89 (1997-03-01)
The object of this review is the genus Proteus, which contains bacteria considered now to belong to the opportunistic pathogens. Widely distributed in nature (in soil, water, and sewage), Proteus species play a significant ecological role. When present in the
Virginie Lecomte et al.
PloS one, 10(5), e0126931-e0126931 (2015-05-21)
The gut microbiota is emerging as a new factor in the development of obesity. Many studies have described changes in microbiota composition in response to obesity and high fat diet (HFD) at the phylum level. In this study we used
D C Morrison et al.
Annual review of medicine, 38, 417-432 (1987-01-01)
In this chapter, current concepts about the mechanisms of action of endotoxin are reviewed. Particular attention is focused upon endotoxin-induced production of soluble mediators from macrophages and mononuclear cells and on the potential contribution of these mediators to endotoxin shock.
J Paul Brooks et al.
BMC microbiology, 15, 66-66 (2015-04-17)
Characterizing microbial communities via next-generation sequencing is subject to a number of pitfalls involving sample processing. The observed community composition can be a severe distortion of the quantities of bacteria actually present in the microbiome, hampering analysis and threatening the
Articles
DNA standards enhance metagenomics research integrity, offering precise species study and mixed community standards.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service