HPLC Analysis of DMB-Labeled Sialic Acids on Ascentis® Express RP-Amide: Comparison of Biosimilars to Reference Materials
Materials
analytical column
CONDITIONS
column
Ascentis® Express RP-Amide, 10 cm x 2.1 mm I,D., 2.7 μm particles (53913-U)
mobile phase
[A] Water, 0.1% formic acid, [B] acetonitrile, 0.1% formic acid
gradient
0-1 min 6% B; 1.01-4 min 20% B;
4.01-12 min 6% B, total run time 15 min
flow rate
0.2 mL/min
pressure
1300 psi (89.6 bar)
column temp.
30 °C
detector
fluorescence, λ excitation = 373 nm, λ emission = 448 nm
injection
0.5 μL
sample
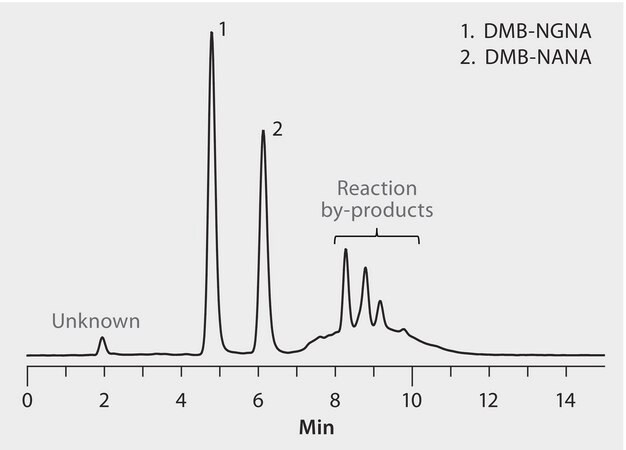
Mix of DMB-labeled NGNA and NANAsialic acid, 5 mg/ml each
Description
Analysis Note
Sialic acids affect the bioavailability, function, stability, and metabolism of glycoproteins. Two forms of sialic acid are commonly present in therapeutic glycoproteins: N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA) and N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NGNA). One of the most common quantification methods involves releasing sialic acids from the glycoprotein, derivatizing NANA and NGNA with 1,2-diamino-4, 5-methylenedioxybenzene (DMB), and analyzing by C18-HPLC with fluorescence detection. This procedure is subject to interference from peaks originating from excess reagent and other derivatized impurities, limiting sensitivity and reproducibility. The objectives of this study were to develop a significantly improved HPLC-fluorescence method for DMB-NANA and DMB-NGNA, and to apply this method to compare two candidate biosimilar therapeutic proteins to their respective reference materials.
Legal Information
Ascentis is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany