RAWP02500
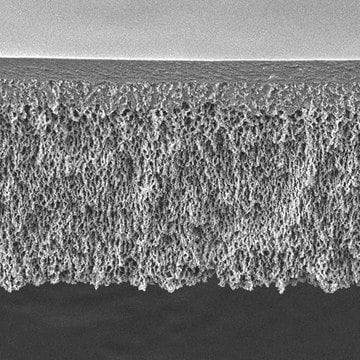
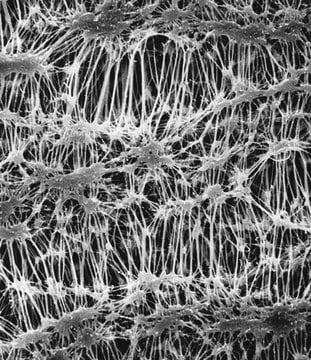
MCEメンブレンフィルター、1.2 μm孔径
MF-Millipore™, filter diam. 25 mm, hydrophilic
別名:
MF-Millipore™メンブレンフィルター、孔径1.2 µm
About This Item
82 % porosity
plain filter
white filter
おすすめの製品
物質
mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane
plain filter
white filter
品質水準
認証
in accordance with NIOSH 7400,7402
in accordance with OSHA ID 160
詳細
25 mm diameter, mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, hydrophilic, white, 100 discs
無菌性
non-sterile
特徴
hydrophilic
メーカー/製品名
MF-Millipore™
Millipore
パラメーター
20 L/min-cm2 air flow rate
270 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate
75 °C max. temp.
フィルタ直径
25 mm
厚さ
150 μm
重量分析抽出物
5%
色
white
屈折率
n/D 1.512
Matrix
MF-Millipore™
ポアサイズ
1.2 μm pore size
82 % porosity
泡立ち点
≥0.76 bar, air with water at 23 °C
輸送温度
ambient
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
詳細
アプリケーション
特徴および利点
- 生物および環境モニタリング用途に適します。
- オートクレーブ可能で、エチレンオキサイドおよびγ線照射滅菌法に適合します。
法的情報
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Flam. Sol. 1
保管分類コード
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
消防法
第5類:自己反応性物質
硝酸エステル類
危険等級I
第一種自己反応性物質
Jan Code
RAWP02500:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)