추천 제품
material
mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane
plain filter
white filter
Quality Level
Agency
in accordance with NIOSH 7400,7402
in accordance with OSHA ID 160
설명
25 mm diameter, mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, hydrophilic, white, 100 discs
무균
non-sterile
특징
hydrophilic
제조업체/상표
MF-Millipore™
Millipore
파라미터
20 L/min-cm2 air flow rate
270 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate
75 °C max. temp.
필터 직경
25 mm
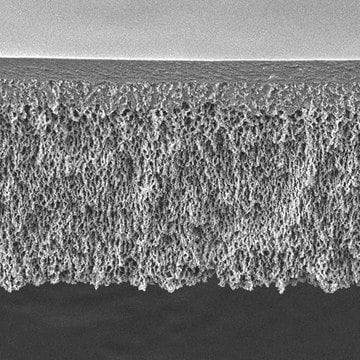
두께
150 μm
중량 추출물
5%
색상
white
refractive index
n/D 1.512
Matrix
MF-Millipore™
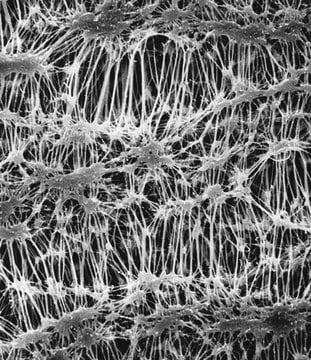
공극 크기
1.2 μm pore size
82 % porosity
버블 포인트(bubble point)
≥0.76 bar, air with water at 23 °C
배송 상태
ambient
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
일반 설명
MF-Millipore™ membrane filters comprising biologically inert mixtures of cellulose acetate and cellulose nitrate have wide use in research and analytical applications.
애플리케이션
Clarification of aqueous solutions
특징 및 장점
- For use in biological and environmental monitoring applications.
- Autoclavable and compatible with ethylene oxide and gamma irradiation sterilization.
법적 정보
MF-Millipore is a trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Sol. 1
Storage Class Code
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
Werner Weitschies et al.
Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society, 108(2-3), 375-385 (2005-10-11)
Gastrointestinal motility and transport as well as concomitant food intake are factors that are known to influence pharmacokinetics derived after intake of extended release dosage forms. However, the mechanisms behind these influencing factors are mostly unknown. In this study the
Claudiu V Giuraniuc et al.
PloS one, 8(5), e64419-e64419 (2013-05-16)
Construction of synthetic genetic networks requires the assembly of DNA fragments encoding functional biological parts in a defined order. Yet this may become a time-consuming procedure. To address this technical bottleneck, we have created a series of Gateway shuttle vectors
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.