All Photos(2)
About This Item
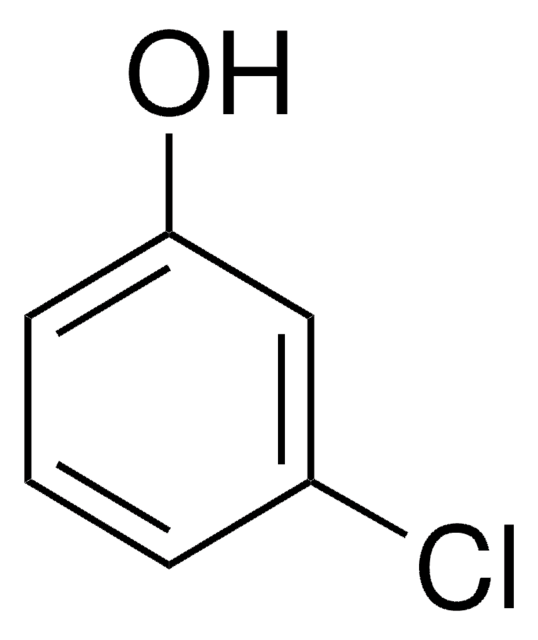
Linear Formula:
ClC6H3(OH)2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
144.56
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
97%
mp
90-94 °C (lit.)
functional group
chloro
SMILES string
Oc1ccc(Cl)cc1O
InChI
1S/C6H5ClO2/c7-4-1-2-5(8)6(9)3-4/h1-3,8-9H
InChI key
WWOBYPKUYODHDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
4-chlorocatechol was a major degradation product of 4-chloro-2-aminophenol (4C2AP). The degradation of 4-chlorocatechol was catalyzed by cphA-I enzyme.
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
A Farrell et al.
Journal of industrial microbiology & biotechnology, 28(6), 316-324 (2002-05-29)
A bacterium, CP1, identified as Pseudomonas putida strain, was investigated for its ability to grow on and degrade mono-chlorophenols and phenols as sole carbon sources in aerobic shaking batch culture. The organism degraded up to 1.56 mM 2- and 3-chlorophenol
Y Samet et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 138(3), 614-619 (2006-07-18)
Electrochemical oxidation of 4-chloroguaiacol (4-CG) at Nb/PbO(2) anodes was studied under different experimental conditions such as initial concentration of substrate, electrolysis time, temperature and pH. We measured the concentrations of 4-chlorocatechol (4-CC), 2-methoxyhydroquinone (2-MHQ), maleic acid (MA) and carbon dioxide
Pankaj Kumar Arora et al.
Environmental science and pollution research international, 21(3), 2298-2304 (2013-09-24)
Burkholderia sp. RKJ 800 utilized 4-chloro-2-aminophenol (4C2AP) as the sole carbon and energy source and degraded it with release of chloride and ammonium ions. The metabolic pathway of degradation of 4C2AP was studied and a novel intermediate, 4-chlorocatechol was identified
Yingxun Du et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 139(1), 108-115 (2006-07-28)
The role of oxygen in the degradation pathway of 4-CP by Fenton system was investigated in this paper. The degradation of 4-CP, changes of Fenton reagent's concentration and formation of the intermediates in Fenton/O2 system were respectively compared with those
M Klemba et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 66(8), 3255-3261 (2000-08-05)
The tcbR-tcbCDEF gene cluster, coding for the chlorocatechol ortho-cleavage pathway in Pseudomonas sp. strain P51, has been cloned into a Tn5-based minitransposon. The minitransposon carrying the tcb gene cluster and a kanamycin resistance gene was transferred to Pseudomonas putida KT2442
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service