383317
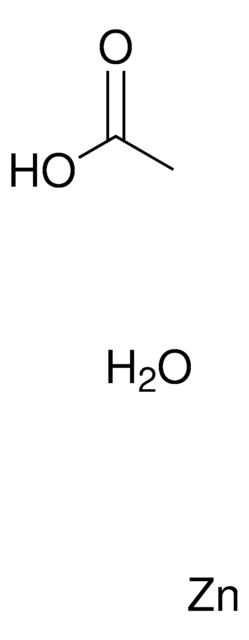
Zinc acetate
99.99% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Zn(OAc)2
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
99.99% trace metals basis
form
solid
reaction suitability
core: zinc
reagent type: catalyst
impurities
<0.2% water
density
1.84 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CC(O[Zn]OC(C)=O)=O
InChI
1S/2C2H4O2.Zn/c2*1-2(3)4;/h2*1H3,(H,3,4);/q;;+2/p-2
InChI key
DJWUNCQRNNEAKC-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
For small scale and high throughput uses, product is also available as ChemBeads (927805)
Application
- Synthesis of layered Zn-arylphosphonates with potential application in sorption, ion exchange or catalysis.
- Ultrasonic preparation of zinc sulfide nanoparticles coated on silica particles.
- Synthesis of ZnO/ZnS composites throughion exchange method (1)
- Fabrication of 3D hierarchical ZnO/ZnSheterojunction branched nanowires for enhanced photoelectrochemical watersplitting (2)
- Synthesis of Co3O4-decorated ZnO@ZnS core-shellstructures for efficient photocatalytic overall water splitting (3)
- Synthesis of ZnO photocatalysts (4)
Preparation Note
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service