54345
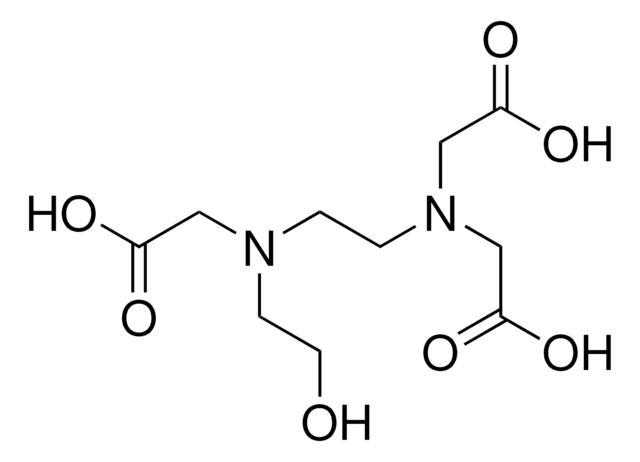
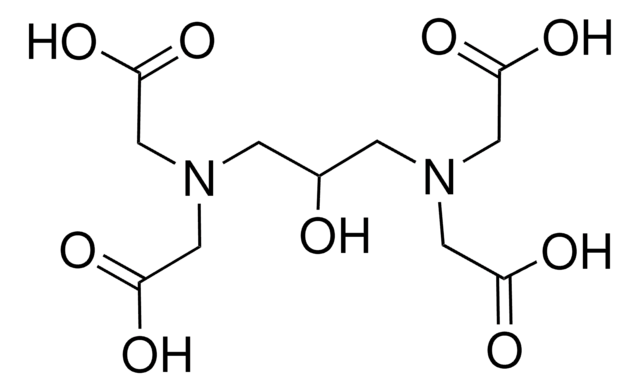
N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)iminodiacetic acid
≥98.0% (T)
Synonym(s):
Ethanol diglycine
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
≥98.0% (T)
form
solid
mp
178 °C (lit.)
application(s)
peptide synthesis
SMILES string
OCCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O
InChI
1S/C6H11NO5/c8-2-1-7(3-5(9)10)4-6(11)12/h8H,1-4H2,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)
InChI key
JYXGIOKAKDAARW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- HEIDA can be used as a metal chelating agent for Fe(III) ion. The presence of HEIDA improves the Fenton′s destruction performance of PCE (perchloroethylene) existing as dense non-aqueous phase liquid (DNAPL) in soil slurry systems.[1]
- Oxorhenium(V) complexes with HEIDA are used for the carboxylation of ethane by CO, with potassium peroxodisulfate (K2S2O8)/trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), to afford propionic and acetic acid in good yield.[2]
- Vanadium complexes with HEIDA are used for the peroxidative hydroxylation of benzene and oxidation of mesitylene.[3]
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service