792551
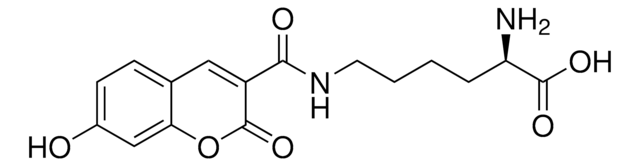
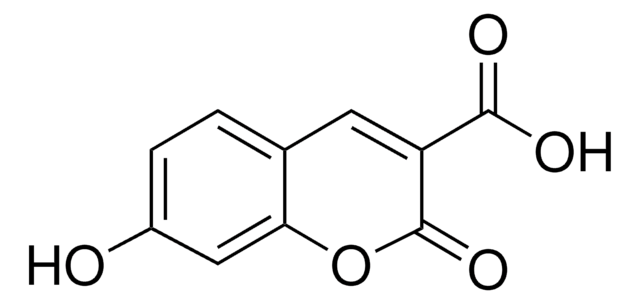
H-4-(7-Hydroxy-4-coumarinyl)-Abu-OH
98% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
(S)-2-Amino-4-(7-hydroxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl)butanoic acid, Schultz Fluorescent UAA
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C13H13NO5
Molecular Weight:
263.25
UNSPSC Code:
12352111
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
98% (HPLC)
form
solid
optical activity
[α]22/D +8.0°, c = 0.5% in 1 M NaOH
mp
276-281 °C
storage temp.
15-25°C
Application
The courmarin-based unnatural amino acid is an effective fluorophore; which has been incoporated into several studies of protein interactions.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Ishu Saraogi et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 133(38), 14936-14939 (2011-08-30)
As newly synthesized proteins emerge from the ribosome, they interact with a variety of cotranslational cellular machineries that facilitate their proper folding, maturation, and localization. These interactions are essential for proper function of the cell, and the ability to study
Timo Koopmans et al.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, 21(2), 553-559 (2012-12-15)
Incorporation of the unnatural amino acid L-(7-hydroxycoumarin-4-yl)ethylglycine (7-HC) is a powerful and reliable approach for the preparation of fluorescently labeled proteins. The growing popularity of this valuable amino acid prompted us to pursue an improved protocol for its synthetic preparation.
Douglas D Young et al.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 21(24), 7502-7504 (2011-11-02)
The site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids (UAAs) into proteins in bacteria is made possible by the evolution of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that selectively recognize and aminoacylate the amino acid of interest. Recently we have discovered that some of the previously
Jiangyun Wang et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 128(27), 8738-8739 (2006-07-06)
The fluorescent amino acid l-(7-hydroxycoumarin-4-yl) ethylglycine 1 has been genetically encoded in E. coli in response to the amber TAG codon. Because of its high fluorescence quantum yield, relatively large Stoke's shift, and sensitivity to both pH and polarity, this
Shengxi Chen et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135(35), 12924-12927 (2013-08-15)
Two fluorescent amino acids, including the novel fluorescent species 4-biphenyl-l-phenylalanine (1), have been incorporated at positions 17 and 115 of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) to enable a study of conformational changes associated with inhibitor binding. Unlike most studies involving fluorescently labeled
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service