926345
NanoFabTx™-DC-Chol Lipid Mix
for synthesis of cationic (DC-cholesterol) liposomes
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Application
NanoFabTx™ lipid mixes and formulation kits enable users to encapsulate a wide variety of therapuetic drug molecules for targeted or extended drug delivery without the need for lengthy trial-and-error optimization. NanoFabTx™ reagent kits provide an easy-to-use toolkit for encapsulating a variety of therapeutics in nanoparticles, microparticles, or liposomes. Drug encapsulated particles synthesized with the NanoFabTx™ kits are suitable for biomedical research applications such as oncology, immuno-oncology, gene delivery, and vaccine delivery.
Features and Benefits
- A ready-to-use nanoformulation blend for the synthesis of cationic DC-cholesterol liposomes
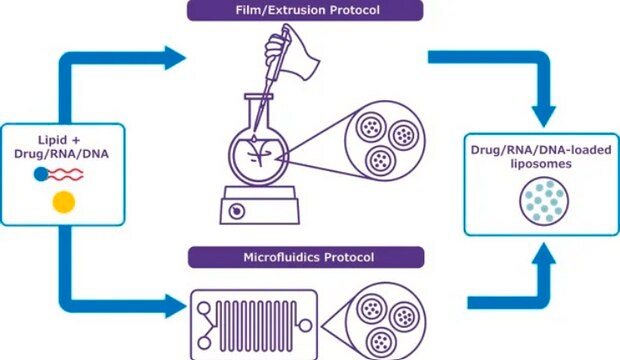
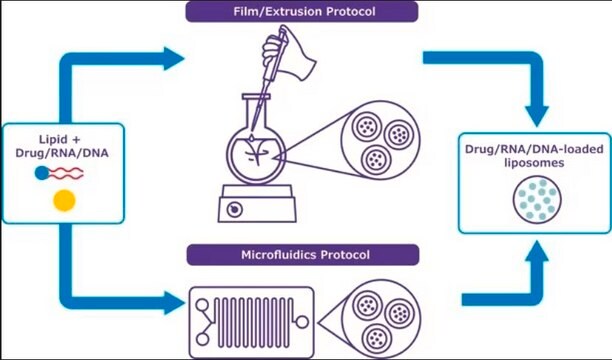
- Step-by-step protocols (extrusion or microfluidic) developed and tested by our formulation scientists
- Flexible synthesis tools to create uniform and reproducible liposomes
- Optimized to make liposomes around 100 nm with low polydispersity
- DC-Cholesterol allows for high transfection efficiency and targeted drug delivery
- A lipid film hydration and extrusion protocol.
- A microfluidics protocol using commercial platforms or syringe pumps.
Legal Information
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service