T511307
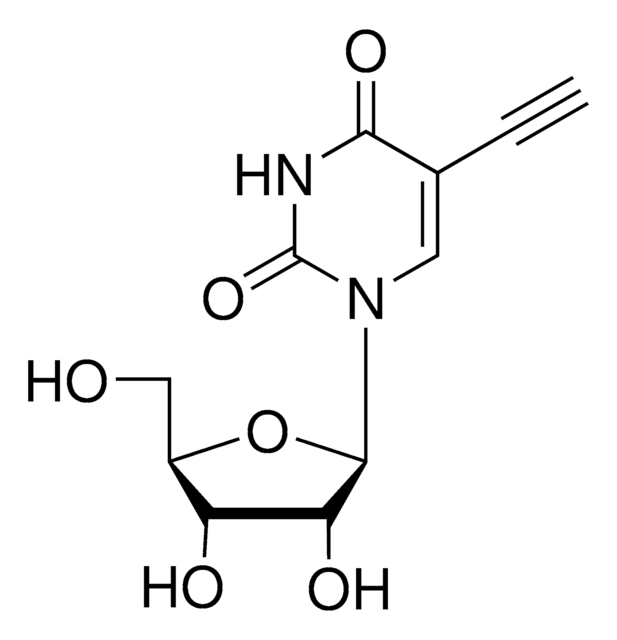
5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxycytidine, (EdC)
AldrichCPR
Synonym(s):
2′-Deoxy-5-ethynylcytidine
About This Item
Recommended Products
reaction suitability
reaction type: click chemistry
SMILES string
NC1=NC(=O)N(C=C1C#C)[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2
InChI
1S/C11H13N3O4/c1-2-6-4-14(11(17)13-10(6)12)9-3-7(16)8(5-15)18-9/h1,4,7-9,15-16H,3,5H2,(H2,12,13,17)/t7-,8+,9+/m0/s1
InChI key
HMJSYXIPNSASJY-DJLDLDEBSA-N
Application
Other Notes
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY CONTRARY PROVISION CONTAINED IN SIGMA-ALDRICH′S STANDARD TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE OR AN AGREEMENT BETWEEN SIGMA-ALDRICH AND BUYER, SIGMA-ALDRICH SELLS THIS PRODUCT "AS-IS" AND MAKES NO REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY WHATSOEVER WITH RESPECT TO THIS PRODUCT, INCLUDING ANY (A) WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY; (B) WARRANTY OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE; OR (C) WARRANTY AGAINST INFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS OF A THIRD PARTY; WHETHER ARISING BY LAW, COURSE OF DEALING, COURSE OF PERFORMANCE, USAGE OF TRADE OR OTHERWISE.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Related Content
Metabolic incorporation of a bioorthogonal functional group (e.g. alkyne, azide, alkene, etc.) into cellular DNA can be achieved by simply adding a synthetic nucleoside to the nutritional media of cells or whole animals.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service