I4401
Interferon-αA/D human
≥95%, recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
IFN-αA/D
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
≥95%
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
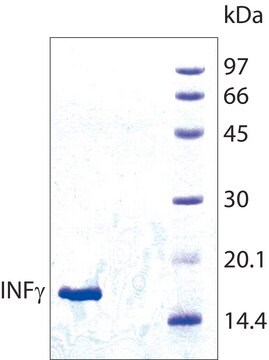
19 kDa
packaging
pkg of 100K units
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
endotoxin, tested
color
colorless
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... IFNA2(3440)
Application
Interferon-αA/D human has been used:
- for identification of coronavirus replicase inhibitors
- in combination with ACH-806 [1-(4-pentyloxy-3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(pyridine-3-carbonyl)thiourea] to study the effect on hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication
- in combination with vitamin D to check reduction in HCV protein production in cell culture
Biochem/physiol Actions
Interferon-αA/D (Bg/II), also known as Universal Type I Interferon, is an α interferon hybrid that crosses the species barrier. The Bg/II denotes the restriction enzyme site from which this hybrid is constructed from recombinant human interferons αA and αD. Interferon-αA/D has been proven to be active on many mammalian cells. It can substitute for human, monkey, mouse, bovine, rat, cat, dog, rabbit, sheep, goat, horse, pig or hamster type I interferon (α, β, ω and τ). Type I Interferons are a closely related family of 165-172 amino acid proteins that are produced by leukocytes (α subtypes), fibroblasts (β subtypes), lymphocytes (ω subtypes), and ruminant embryos (τ subtypes). This cytokine has anti-viral, anti-proliferative, immunoregulatory, and proinflammatory activities.
This cytokine has anti-viral, anti-proliferative, immunoregulatory, and proinflammatory activities.
Physical form
Solution in phosphate buffered saline containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin
Analysis Note
The biological activity is determined in the cytopathic effect inhibition assay using MDBK cells with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). A cytopathic effect of 50% is produced with 1 unit/ml interferon. The units are determined with respect to NIH international standard reference for human interferonαA.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Pathompong Bowornruangrit et al.
Medical sciences (Basel, Switzerland), 10(1) (2022-03-25)
Autophagy is a known mechanism of cells under internal stress that regulates cellular function via internal protein recycling and the cleaning up of debris, leading to healthy live cells. However, the stimulation of autophagy by external factors such as chemical
C Lauber et al.
Genes and immunity, 16(6), 414-421 (2015-06-13)
The IFNL4 gene is negatively associated with spontaneous and treatment-induced clearance of hepatitis C virus infection. The activity of IFNλ4 has an important causal role in the pathogenesis, but the molecular details are not fully understood. One possible reason for
Ronald Dijkman et al.
Journal of virology, 96(11), e0036422-e0036422 (2022-05-20)
Effective broad-spectrum antivirals are critical to prevent and control emerging human coronavirus (hCoV) infections. Despite considerable progress made toward identifying and evaluating several synthetic broad-spectrum antivirals against hCoV infections, a narrow therapeutic window has limited their success. Enhancing the endogenous
Guido Wollmann et al.
Journal of virology, 89(13), 6711-6724 (2015-04-17)
High-grade tumors in the brain are among the deadliest of cancers. Here, we took a promising oncolytic virus, vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), and tested the hypothesis that the neurotoxicity associated with the virus could be eliminated without blocking its oncolytic
David L Wyles et al.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 52(5), 1862-1864 (2008-03-12)
Rapid emergence of resistance to monotherapy with virus-specific inhibitors necessitates combination therapy. ACH-806 is a hepatitis C virus NS4A inhibitor with a novel mechanism of action and resistance pathway. This compound was synergistic with NS3 protease inhibitors and NS5B nucleoside
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service