I7634
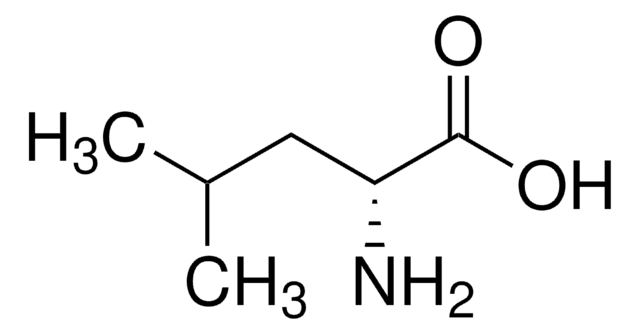
D-Isoleucine
≥98% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
(2R, 3R)-2-Amino-3-methylpentanoic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C2H5CH(CH3)CH(NH2)CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
131.17
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
Product Name
D-Isoleucine, ≥98% (TLC)
Quality Level
assay
≥98% (TLC)
form
powder
impurities
≤10% allo-isomer
color
white
application(s)
cell analysis
SMILES string
CC[C@@H](C)[C@@H](N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C6H13NO2/c1-3-4(2)5(7)6(8)9/h4-5H,3,7H2,1-2H3,(H,8,9)/t4-,5-/m1/s1
InChI key
AGPKZVBTJJNPAG-RFZPGFLSSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
- Metabolic Profiling of Urinary Chiral Amino-Containing Biomarkers for Gastric Cancer Using a Sensitive Chiral Chlorine-Labeled Probe by HPLC-MS/MS.: This study by Huang et al. (2021) explores the use of D-Isoleucine as a biomarker for gastric cancer, utilizing advanced metabolic profiling techniques with HPLC-MS/MS to detect chiral amino-containing compounds in urine samples (Huang et al., 2021).
- Isopenicillin N Synthase Binds δ-(L-α-aminoadipoyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-thia-allo-isoleucine Through Both Sulfur Atoms.: Clifton et al. (2011) describe the binding mechanism of Isopenicillin N synthase with a compound involving D-Isoleucine, highlighting its role in antibiotic biosynthesis and enzyme interaction studies (Clifton et al., 2011).
- The Total Structure of the Antibiotic Longicatenamycin.: Shiba and Mukunoki (1975) determined the complete structure of the antibiotic longicatenamycin, which includes D-Isoleucine as a crucial component, contributing to understanding its antibacterial properties (Shiba and Mukunoki, 1975).
Biochem/physiol Actions
D-Isoleucine may be used to help characterize and differentiate various D-amino acid oxidases. D-Isoleucine may be used to differentiate the activities of D- and L-isoleucine in processes such as the induction of pigmentation in B16F0 melanoma cells.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Shouji Takahashi et al.
Journal of biochemistry, 159(3), 371-378 (2015-11-01)
D-Aspartate oxidase (DDO) catalyzes the oxidative deamination of acidic D-amino acids, whereas neutral and basic D-amino acids are substrates of D-amino acid oxidase (DAO). DDO of the yeast Cryptococcus humicola (ChDDO) has much higher substrate specificity to D-aspartate, but the
A Gholizadeh et al.
Biochemistry. Biokhimiia, 74(2), 137-144 (2009-03-10)
D-Amino acid oxidase (DAAO) is an FAD-dependent enzyme that metabolizes D-amino acids in microbes and animals. However, such ability has not been identified in plants so far. We predicted a complete DAAO coding sequence consisting of 1158 bp and encoding
Masago Ishikawa et al.
Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin, 30(4), 677-681 (2007-04-06)
Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, play significant roles in numerous physiological events in mammals. As the effects of amino acids on melanogenesis have yet to be demonstrated, the present study was conducted to identify whether amino acids, in
Molecular aggregation in selected crystalline 1:1 complexes of hydrophobic D- and L-amino acids. IV. The L-phenylalanine series.
Gorbitz CH, Rissanen K, Valkonen A, Husab? A.
Acta Crystallographica Section C, Crystal Structure Communications, 65, 267-272 (2009)
Ivan Kashkan et al.
Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 9(7) (2020-07-12)
Rapid progress in plant molecular biology in recent years has uncovered the main players in hormonal pathways and characterized transcriptomic networks associated with hormonal response. However, the role of RNA processing, in particular alternative splicing (AS), remains largely unexplored. Here
Chromatograms
application for HPLCOur team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service