M3692
Anti-MRP2 antibody, Mouse monoclonal
clone CPR96, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Synonym(s):
Anti-ABCC2, Anti-Multidrug Resistance Associated Protein 2, Anti-cMOAT, Anti-cMRP
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
CPR96, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
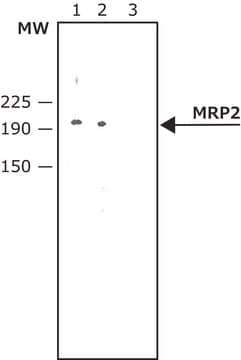
antigen ~180 kDa
species reactivity
human
concentration
~1.5 mg/mL
General description
Anti-MRP2 antibody, Mouse monoclonal (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the CPR96 hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells (NS1) and splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with a synthetic peptideintestine.
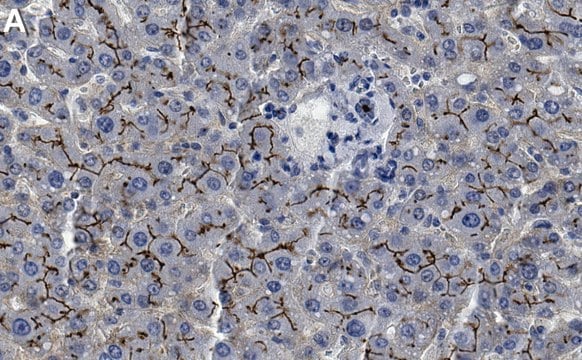
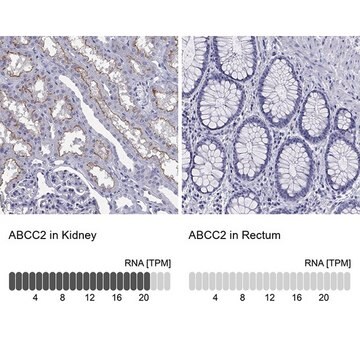
The gene MRP2 (Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein 2), also referred to as ABCC2 (ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 2), encodes a glycosylated protein belonging to the subfamily of MRP efflux pumps, the members of which are localized exclusively to the apical membrane domain of polarized cells, such as hepatocytes, renal proximal tubule epithelia, and intestinal epithelia. The protein consists of 1545 aa residues having a molar mass of ∼190 kDa. The gene with 32 exons is mapped to human chromosome 10q24.
Application
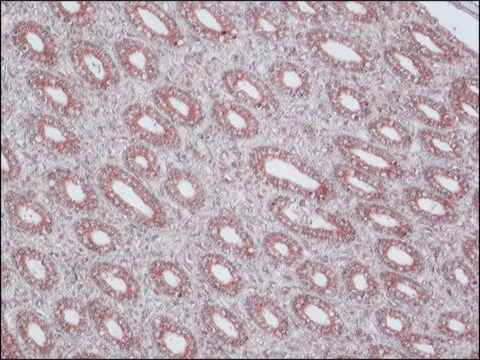
Anti-MRP2 antibody, Mouse monoclonal has been used in:
- western blotting
- immunohistochemistry
- immunofluorescence microscopy
- enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein 2 (MRP2) contributes to bile flow and plays a detoxification role and provides protection against oxidative stress. Upregulation of MRP2 expression may be found in hepatocellular carcinomas.
The gene MRP2 (Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein 2) encodes a protein involved in organic anion efflux. It is involved in biliary transport and the efflux of many conjugated compounds across the apical membrane of the hepatocyte into the bile canaliculi. It also participates in multi-drug resistance in mammalian cells. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Dubin-Johnson syndrome (DJS), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by an increased concentration of bilirubin glucuronosides in blood.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Role of Nrf2 in the regulation of the Mrp2 (ABCC2) gene
Vollrath V, et al.
The Biochemical Journal, 395(3), 599-609 (2006)
High activity P-gp, MRP2 and BCRP membrane vesicles prepared from transiently transfected HEK293-EBNA cells
Karlsson JE, et al.
Drug Metabolism and Disposition, dmd-109 (2010)
Molecular characterization of the NPC1L1 variants identified from cholesterol low absorbers
Wang LJ, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(9), 7397-7408 (2011)
Heidi R Kast et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 277(4), 2908-2915 (2001-11-14)
The multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2, ABCC2), mediates the efflux of several conjugated compounds across the apical membrane of the hepatocyte into the bile canaliculi. We identified MRP2 in a screen designed to isolate genes that are regulated by the
Vasilis Vasiliou et al.
Human genomics, 3(3), 281-290 (2009-05-01)
There exist four fundamentally different classes of membrane-bound transport proteins: ion channels; transporters; aquaporins; and ATP-powered pumps. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are an example of ATP-dependent pumps. ABC transporters are ubiquitous membrane-bound proteins, present in all prokaryotes, as well as
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service