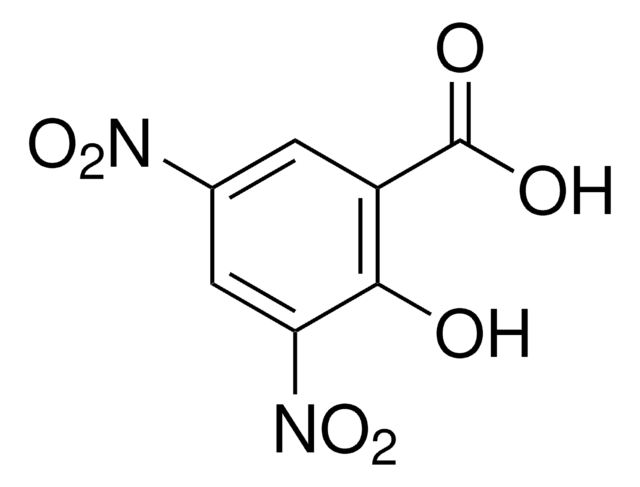
P9792
Phytase from Aspergillus ficuum
lyophilized powder, 1-5 units/mg solid (as phosphatase activity)
Synonym(s):
3-Phytase, myo-Inositol-hexakisphosphate 3-phosphohydrolase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
1-5 units/mg solid (as phosphatase activity)
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Quality
May contain glucosidases and phosphatases.
Unit Definition
One unit will liberate 1.0 μmole of inorganic P from 4.2 × 10-2 M Mg·K phytate per min at pH 2.5 at 37 °C.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
G C Irving et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 112(1), 434-438 (1972-10-01)
The fungus Aspergillus ficuum NRRL 3135 is known to produce an extracellular nonspecific orthophosphoric monoester phosphohydrolase (EC 3.1.3.2) with a pH optimum of 2.0, as well as an extracellular myo-inositol hexaphosphate phosphohydrolase (EC 3.1.3.8; phytase) with pH optima of 2.0
L Jermutus et al.
Journal of biotechnology, 85(1), 15-24 (2001-02-13)
Thermostability is a key feature for commercially attractive variants of the fungal enzyme phytase. In an initial set of experiments, we restored ionic interactions and hydrogen bonds on the surface of Aspergillus terreus phytase, which are present in the homologous
Duane F Berry et al.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 15(12), 3157-3161 (2005-05-10)
A novel approach for measuring phytase activity is presented. We have developed a new chromophoric substrate analog of phytic acid, 5-O-[6-(benzoylamino)hexyl]-d-myo-inositol-1,2,3,4,6-pentakisphosphate that permits direct measurement of the phosphate ester bond-cleavage reaction using HPLC. This compound, along with its dephosphorylated T-phosphatidylinositol
Molecular and physiological characterisation of a 3-phytase from soil bacterium Klebsiella sp. ASR1.
A Sajidan et al.
Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 65(1), 110-118 (2004-01-17)
Klebsiella sp. strain ASR1 isolated from an Indonesian rice field is able to hydrolyse myo-inositol hexakis phosphate (phytate). The phytase protein was purified and characterised as a 42 kDa protein accepting phytate, NADP and sugar phosphates as substrates. The corresponding
J Dvoráková et al.
Folia microbiologica, 45(2), 128-132 (2001-03-29)
Kinetics of phytate hydrolysis by Aspergillus niger phytase and correlation between the amount of released phosphate and creation of lower myo-inositol phosphates were investigated. Phytase was able to hydrolyze myo-inositol hexakis-, pentakis-, tetrakis-, and trisphosphates. Finally, about 56% of total
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service