S8633
Sphingomyelinase from Staphylococcus aureus
buffered aqueous glycerol solution, 100-300 units/mg protein (Lowry)
Synonym(s):
Sphingomyelin choline phosphohydrolase, Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
Quality Level
specific activity
100-300 units/mg protein (Lowry)
storage temp.
2-8°C
Application
Sphingomyelinase from Staphylococcus aureus has been used to:
- induce neurotoxicity in rat cortical cultures to study the protective effects of minocycline
- determine the concentration of sphingomyelin from serum samples
- enhance sphingomyelinase activity to study PARK9-mediated exosome biogenesis
Biochem/physiol Actions
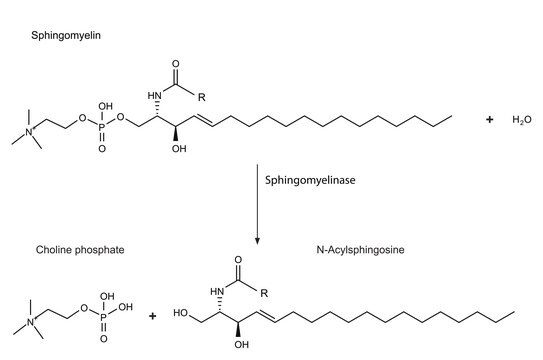
Bacterial sphingomyelinase is active at neutral pH. When used in cell culture in vitro, it hydrolyzes the sphingomyelin on the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane and produces ceramide that is lipid-soluble. Sphingomyelinase is the key enzyme in the sphingomyelinase/ceramide pathway, which is implicated in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative disorders.
Initiates the formation of sphingomyelin-based second messengers. Activates MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) and SAPKs (stress-activated protein kinases); generates ceramide from sphingomyelin.
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmol of TNPAL-sphingomyelin per min at pH 7.4 at 37 °C.
Physical form
Solution in 50% glycerol containing 0.25 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.5
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Measurement of sphingomyelin and ceramide cellular levels after sphingomyelinase-mediated sphingomyelin hydrolysis.
P Santana et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 105, 217-221 (1999-07-31)
Taiji Tsunemi et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 34(46), 15281-15287 (2014-11-14)
Kufor-Rakeb syndrome (KRS) is caused by loss-of-function mutations in ATP13A2 (PARK9) and characterized by juvenile-onset parkinsonism, pyramidal signs, and cognitive decline. Previous studies suggested that PARK9 deficiency causes lysosomal dysfunction and α-synuclein (α-syn) accumulation, whereas PARK9 overexpression suppresses toxicity of
Elin Rebecka Carlsson et al.
Frontiers in endocrinology, 9, 172-172 (2018-06-21)
Metabolic surgery is superior to lifestyle intervention in reducing weight and lowering glycemia and recently suggested as treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Especially Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) has been focus for much research, but still the mechanisms of action
Feixiang Wang et al.
The Journal of clinical investigation, 131(19) (2021-08-18)
Proper metabolic activities facilitate T cell expansion and antitumor function; however, the mechanisms underlying disruption of the T cell metabolic program and function in the tumor microenvironment (TME) remain elusive. Here, we show a zinc finger protein 91-governed (ZFP91-governed) mechanism
Ching-Min Tang et al.
Free radical biology & medicine, 50(6), 710-721 (2010-12-28)
In this study, we determined whether minocycline may protect rat cortical cultures against neurotoxicity induced by sphingomyelinase/ceramide and explored the underlying mechanisms. We found that minocycline exerted strong neuroprotective effects against toxicity induced by bacterial sphingomyelinase and synthetic C2 ceramide.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service