Recommended Products
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
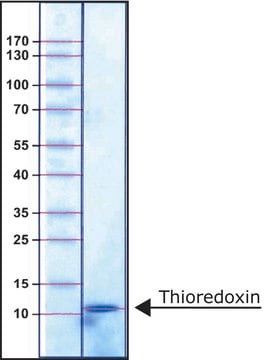
≥95% (SDS-PAGE and HPLC)
form
lyophilized powder
mol wt
31 kDa
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
color
white
application(s)
detection
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... SOD1(6647)
General description
Research Area: Cell Signaling
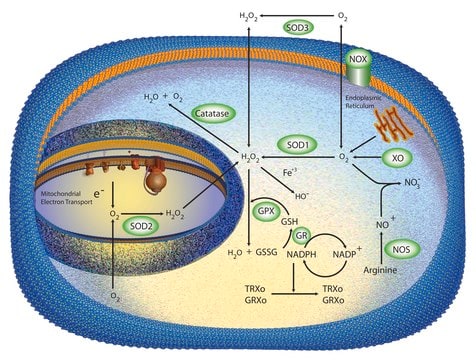
Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) is an intracellular antioxidant enzyme. A mature, functional human SOD1 is a relatively small (32 kDa) homodimeric metalloprotein.
Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) is an intracellular antioxidant enzyme. A mature, functional human SOD1 is a relatively small (32 kDa) homodimeric metalloprotein.
Application
Superoxide Dismutase I human has been used to treat THP-1 (human leukemia monocytic cell line) or human primary macrophage cells to confirm signal specificity for superoxide.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) regulates basal levels of oxidative stress arising from the production of mitochondrial and cytosolic superoxide (O2 .−). Its high cytosolic abundance makes it unique from the other two human superoxide dismutases. SOD1 was believed to be a copper (Cu) storage protein, however, the crucial role of SOD1 is to act as an intracellular antioxidant. SOD1 also initiates gene transcription following exposure to neurotoxic stimuli and modulates signal transduction pathways involving reactive oxygen species (ROS). However, it is also implicated in multiple molecular mechanisms of cytotoxicity, contributing to pathology in diseases such as heart failure, cancer, diabetes, Down′s syndrome, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Parkinson′s disease.
Physical properties
Recombinant Superoxide Dismutase I is fully biologically active when compared to standard.
Reconstitution
Reconstitute in H2O to a concentration of ≥100 μg/ml. The solution can then be diluted into other aqueous buffers.
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Superoxide dismutases.
I Fridovich
Annual review of biochemistry, 44, 147-159 (1975-01-01)
S J Collins et al.
The Journal of experimental medicine, 149(4), 969-974 (1979-04-01)
The HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cell line can be induced to terminally differentiate to mature myeloid cells sharing a number of functional characteristics with normal granulocytes including response to chemoattractants, development of complement receptors, phagocytosis, superoxide production, and nitroblue tetrazolium
S R Jolly et al.
Circulation research, 54(3), 277-285 (1984-03-01)
Therapy directed against the toxic effects of reactive oxygen species may reduce the final extent of ischemic injury in otherwise viable tissue irreversibly injured by the abrupt reoxygenation of reperfusion. In four groups of dogs, superoxide dismutase plus catalase (groups
J S Pollock et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 88(23), 10480-10484 (1991-12-01)
The particulate enzyme responsible for the synthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor has been purified from cultured and native (noncultured) bovine aortic endothelial cells. Purification of the solubilized particulate enzyme preparation by affinity chromatography on adenosine 2',5'-bisphosphate coupled to Sepharose followed
Distinct redox signalling following macrophage activation influences profibrotic activity
Lewis CV, et al.
Journal of immunology research (2019)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service