SML1657
Gefitinib
≥98% (HPLC), powder, EGFR TK inhibitor
Synonym(s):
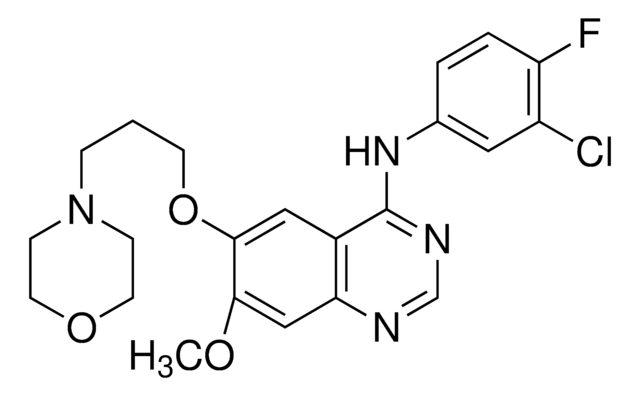
N-(3-Chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine, ZD1839
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Gefitinib, ≥98% (HPLC)
Quality Level
assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
powder
color
white to beige
solubility
DMSO: 10 mg/mL, clear
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
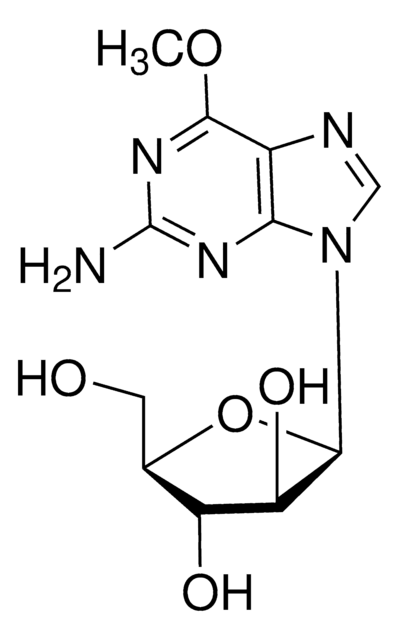
COC(C=C(N=CN=C1NC2=CC(Cl)=C(F)C=C2)C1=C3)=C3OCCCN4CCOCC4
InChI
1S/C22H24ClFN4O3/c1-29-20-13-19-16(12-21(20)31-8-2-5-28-6-9-30-10-7-28)22(26-14-25-19)27-15-3-4-18(24)17(23)11-15/h3-4,11-14H,2,5-10H2,1H3,(H,25,26,27)
InChI key
XGALLCVXEZPNRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
human ... EGFR(1956)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- To study its effective use in endometrial cancer therapy
- Cell proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis assays
- Cell viability assay and colony formation assay
Biochem/physiol Actions
Gefitinib has a higher affinity for ATP (adenosine triphosphate) binding site in the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain than ATP. Hence, gefitinib is known to inhibit the progression of endometrial cancer.
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Carc. 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Repr. 1B - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Storage Class
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service