Assay of Ibuprofen Esters & Impurities
Paul Lee, Jenna Milliken
MilliporeSigma Laramie, WY
Read more about
INTRODUCTION
Ibuprofen, the active pharmaceutical ingredient in many brand-named products, is one of the most prolific APIs on the market and in our households. This application note describes an analysis of Ibuprofen-related compounds and impurities using an HPLC method similar to the compendial method described by the United States Pharmacopeia and European Pharmacopeia. The described ibuprofen assay method separates ibuprofen from various esters and intermediate impurities on the solid-core Ascentis® Express 90Å C18 column (USP L1) with 0.1% phosphoric acid in both water and acetonitrile as mobile phase. Due to the low absorbance maximum for ibuprofen at 220 nm, a slower gradient maximizes the separation and minimizes baseline drift.
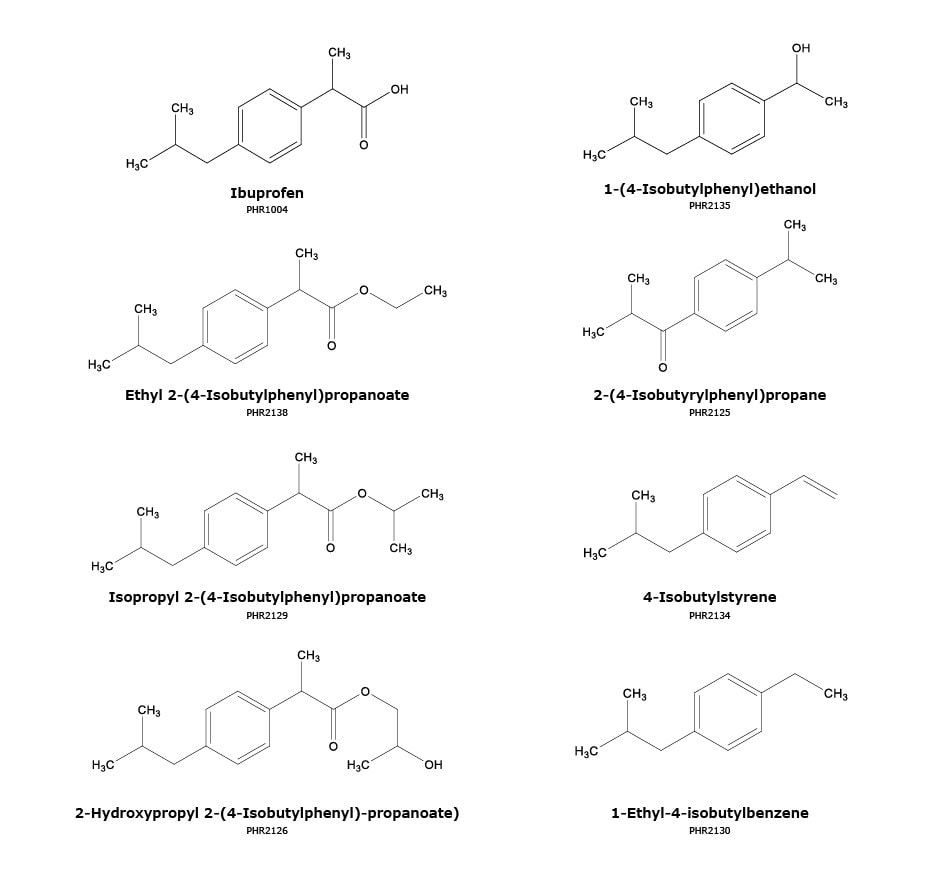
Figure 1.Chemical structures of ibuprofen and ibuprofen-related impurities.
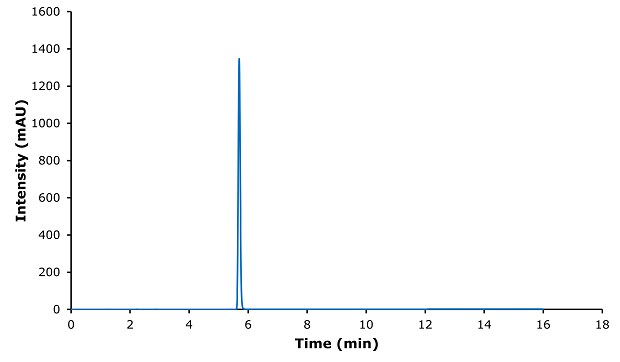
Figure 2.Chromatogram of ibuprofen standard 0.4 mg/mL.
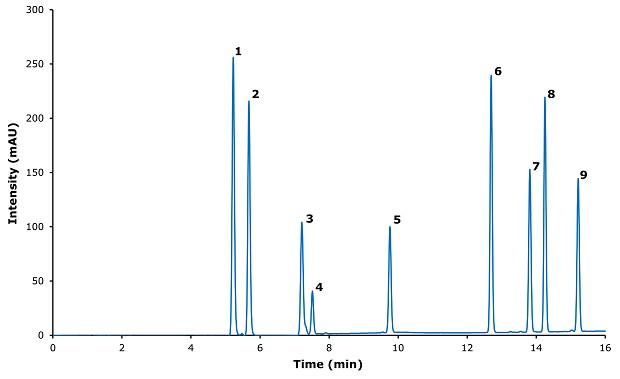
Figure 3.Chromatogram for ibuprofen and its related impurities.
TABLE 1. CHROMATOGRAPHIC AND DETECTION DATA FOR IBUPROFEN ANDITS RELATED IMPURITIES
Calibration and Linearity Data for Ibuprofen and its Related Compounds
Table 2. Calibration data for ibuprofen and its related impurities
Table 3. Linearity - ibuprofen and its impurities
CONCLUSION
This method demonstrates excellent resolution for Ibuprofen and ibuprofen-impurities. But the stereochemical identification was not included in the scope of the analysis conducted (2-Hydroxypropyl 2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)propanoate comprises two diastereoisomers as synthesized).
The maximal range of linearity is approximately 500 µg/mL, particularly for 2-(4-Isobutyrylphenyl)propane and 4-Isobutylstyrene, which have strong absorption at 254 nm rather than 220 nm. The method enables ibuprofen to be separated from its impurities with excellent peak shape, with limits of quantification of 1 µg/mL or less.
See also Small Molecules Analysis & Quality Control (QC) for more information on other applications or use our chromatogram search.
See more chromatograms on ibuprofen here.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?