おすすめの製品
詳細
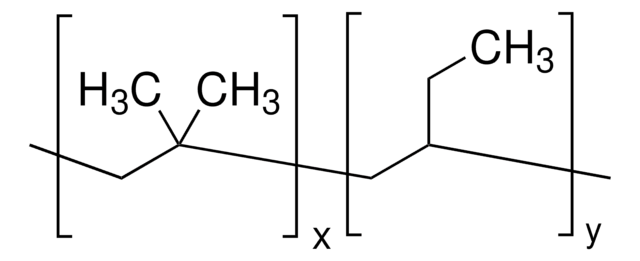
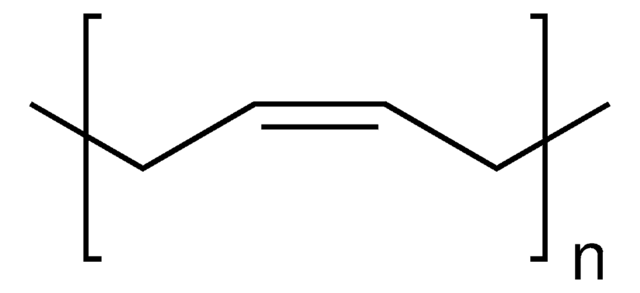
ポリイソブチレンは、無毒な疎水性ポリマーで、 室温での優れた柔軟性、生体内安定性、 生体適合性を発揮します。量子ドットのカプセル化やさまざまな生物医学用途のためのポリマーマトリクスとして使用できます 。
アプリケーション
- 眼科領域におけるポリイソブチレン系ポリマーの使用:眼科用デバイスにおけるポリイソブチレン系ポリマーの用途について説明し、生物医学的用途における可能性を示しています(L Pinchuk, 2022)。
- ポリイソブチレン標識fac-Ir(ppy)3錯体の合成と、連続フロープロセスにおけるリサイクル可能な可視光光触媒としての用途:光駆動化学反応におけるリサイクル可能性と効率を高める、光触媒の担体としてのポリイソブチレンの新規使用法を紹介しています(D Rackl, P Kreitmeier, O Reiser, 2016)。
- 高分子心臓弁尖を製造するためのポリイソブチレン系熱可塑性エラストマー:In vitroおよびIn vivoの結果:心臓弁尖の製造におけるポリイソブチレン系エラストマーの使用を検討し、その物理的特性および適合性を評価しています(E Ovcharenko et al., 2019)。
- ポリイソブチレンの医療用途における新たな機会:ポリイソブチレンの医療資材としての特性や利点に焦点を当て、さまざまな医療用途におけるポリイソブチレンの可能性をレビューしています(D Barczikai et al., 2021)。
- 反応性の高いポリイソブチレンを合成するための均一かつ不均一な触媒:発見、開発、展望:高性能材料に不可欠な、反応性の高いポリイソブチレンを製造するための触媒技術の進歩について論じています(IV Vasilenko, SV Kostjuk, 2021)。
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
181455-250G-PW:
181455-100G-PW:
181455-250G:
181455-25G:
181455-VAR:
181455-BULK:
181455-100G:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
David Cozzens et al.
Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids, 27(23), 14160-14168 (2011-10-26)
The surface properties and biocompatibility of a class of thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs) with applications in blood-contacting medical devices have been studied. Thin films of commercial TPUs and novel polyisobutylene (PIB)-poly(tetramethylene oxide) (PTMO) TPUs were characterized by contact angle measurements, X-ray
Goy Teck Lim et al.
Biomacromolecules, 12(5), 1795-1799 (2011-04-01)
This paper is the first report of electrospinning neat polyisobutylene-based thermoplastic elastomers. Two generations of these materials are investigated: a linear poly(styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene) (L_SIBS) triblock copolymer and a dendritic poly(isobutylene-b-p-methylstyrene) (D_IB-MS), also a candidate for biomedical applications. Cross-polarized optical microscopy shows
David Cozzens et al.
Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A, 95(3), 774-782 (2010-08-21)
Long term in vitro biostability of thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs) containing mixed polyisobutylene (PIB)/poly(tetramethylene oxide) (PTMO) soft segment was studied under accelerated conditions in 20% H(2)O(2) solution containing 0.1M CoCl(2) at 50 °C to predict resistance to metal ion oxidative degradation
M Engel et al.
The Journal of chemical physics, 132(22), 224502-224502 (2010-06-17)
We present results of in situ measurements of the filling process of polymer melts in nanopores. After accurate characterization of the empty nanopores, they are filled with the hydrophobic polyisobutylene and the hydrophilic poly-epsilon-caprolactone. The filling process is investigated in
Jinping Dong et al.
Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids, 25(10), 5442-5445 (2009-05-13)
Drug release from therapeutic biomedical films such as drug-polymer composite coatings on drug eluting stents is a highly complex and poorly understood process. The dynamics of drug release and the evolution of surface morphology during release have direct impact on
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)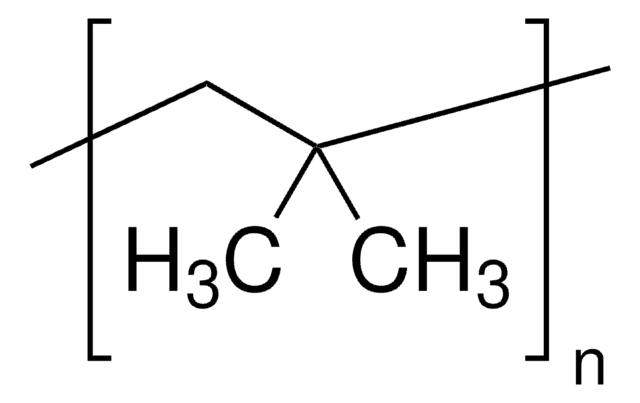




![Poly[(isobutylene-alt-maleic acid, ammonium salt)-co-(isobutylene-alt-maleic anhydride)] average Mw ~60,000](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/208/717/cfb2dcac-b112-4e25-9140-f3649ec430ea/640/cfb2dcac-b112-4e25-9140-f3649ec430ea.png)