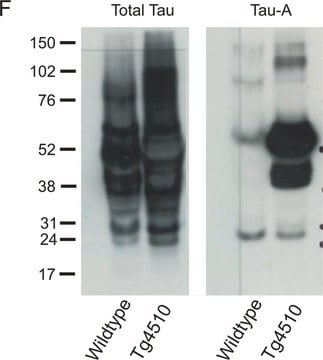
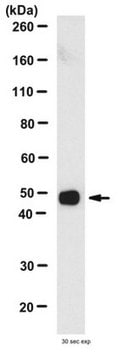
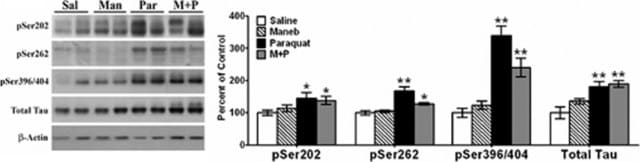
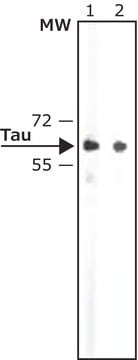
おすすめの製品
由来生物
mouse
品質水準
抗体製品の状態
purified antibody
抗体製品タイプ
primary antibodies
クローン
TAU-5, monoclonal
形状
liquid
含まれません
preservative
化学種の反応性
mouse, human, sheep, rat
メーカー/製品名
Calbiochem®
保管条件
OK to freeze
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
アイソタイプ
IgG1
輸送温度
wet ice
保管温度
−70°C
ターゲットの翻訳後修飾
unmodified
遺伝子情報
human ... MAPT(4137)
mouse ... Mapt(17762)
rat ... Mapt(29477)
詳細
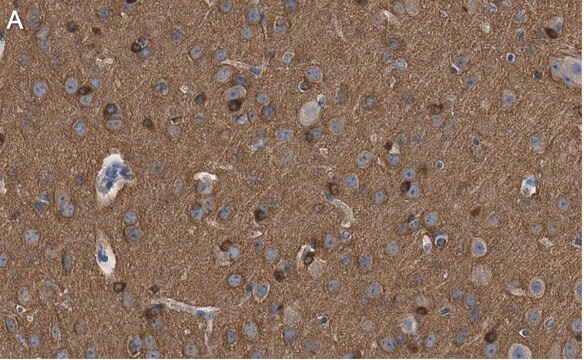
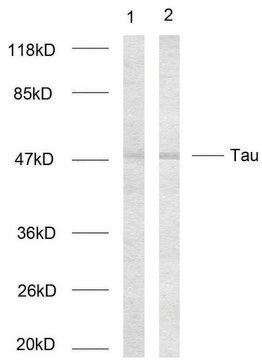
Protein G purified mouse monoclonal antibody. Recognizes the ~45-68 kDa phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of tau.
Recognizes the ~45-68 kDa Tau protein.
This Anti-Tau Mouse mAb (TAU-5) is validated for use in Frozen Sections, Immunoblotting, Immunoprecipitation, Paraffin Sections for the detection of Tau.
免疫原
Bovine
Epitope: within the central region
purified bovine microtubule-associated proteins
アプリケーション
Frozen Sections (1-2 µg/ml)
Immunoblotting (1 µg/ml)
Immunoprecipitation (10 µg per 200-500 µg cell lysate)
Paraffin Sections (1-2 µg/ml, heat pre-treatment required)
Immunoblotting (1 µg/ml)
Immunoprecipitation (10 µg per 200-500 µg cell lysate)
Paraffin Sections (1-2 µg/ml, heat pre-treatment required)
包装
Please refer to vial label for lot-specific concentration.
警告
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
物理的形状
In PBS.
再構成
Following initial thaw, aliquot and freeze (-70°C). Do not store diluted antibody without carrier protein if the concentration is <50 µg/ml.
その他情報
Papasozomenos, S.C. and Shanavas, A., 2002. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA99, 1140.
Rapoport, M., eta al. 2002. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA99, 6364.
Rapoport, M., eta al. 2002. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA99, 6364.
When used for formalin/paraffin embedded sections, staining is enhanced by boiling tissue sections in 10 mM citrate buffer, pH 6.0, for 10-20 min followed by cooling at room temperature for 20 min prior to antibody incubation. Alternate splicing of tau mRNA and differential phosphorylation contribute to the heterogeneity of tau. Does not cross-react with other MAPS of tubulin. Recognizes both native and phosphorylated forms of tau. Variables associated with assay conditions will dictate proper working dilution.
法的情報
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
適切な製品が見つかりませんか。
製品選択ツール.をお試しください
保管分類コード
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
577801-100UG:
577801-UG:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
Ricardo Gargini et al.
Frontiers in aging neuroscience, 11, 231-231 (2019-09-26)
The analysis of global and comparative genomics between different diseases allows us to understand the key biological processes that explain the etiology of these pathologies. We have used this type of approach to evaluate the expression of several neurodegeneration-related genes
Ram Fridlich et al.
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP, 8(6), 1206-1218 (2009-03-13)
Rod-derived cone viability factor (RdCVF) is produced by the Nxnl1 gene that codes for a second polypeptide, RdCVFL, by alternative splicing. Although the role of RdCVF in promoting cone survival has been described, the implication of RdCVFL, a putative thioredoxin
Weijiang Dong et al.
Journal of neuroscience research, 87(14), 3176-3185 (2009-05-28)
Tau function is regulated by phosphorylation, and abnormal tau phosphorylation in neurons is one of the key processes associated with development of Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. In this study we provide evidence that phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP), one of
Michael Dumbacher et al.
Molecular neurodegeneration, 13(1), 50-50 (2018-09-28)
Neuronal Ca2+ dyshomeostasis and hyperactivity play a central role in Alzheimer's disease pathology and progression. Amyloid-beta together with non-genetic risk-factors of Alzheimer's disease contributes to increased Ca2+ influx and aberrant neuronal activity, which accelerates neurodegeneration in a feed-forward fashion. As
Marta Fernández-Nogales et al.
Brain pathology (Zurich, Switzerland), 27(3), 314-322 (2016-06-25)
Increased incidence of neuronal nuclear indentations is a well-known feature of the striatum of Huntington's disease (HD) brains and, in Alzheimer's disease (AD), neuronal nuclear indentations have recently been reported to correlate with neurotoxicity caused by improper cytoskeletal/nucleoskeletal coupling. Initial
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)