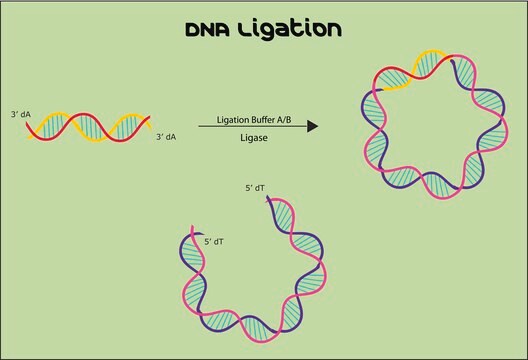
おすすめの製品
グレード
for molecular biology
品質水準
形状
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
比活性
4,000 U/mL
分子量
68 kDa
UniProtアクセッション番号
保管温度
−20°C
遺伝子情報
bacteriophage T4 ... 30(1258680)
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
関連するカテゴリー
アプリケーション
0.01 Weiss unitは、16°C、20分間に、1 μgのバクテリオファージλHind IIIフラグメントの95%以上を連結するために必要な酵素量です。
生物化学的/生理学的作用
T4 DNAリガ-ゼは、近接の2重鎖DNAのポリヌクレオチド末端間における、エネルギ-依存性のホスホジエステル結合を形成します。この結合反応には補因子としてATPが必要です。平滑末端断片の結合には、高い酵素濃度を必要となります。反応混合物にPEGを使用するとこの反応が促進されます。 本酵素は 3′末端の水酸基と5′末端のリン酸基を結合します。アルカリホスファタ-ゼの脱リン酸化でベクタ-DNAの自己結合を回避できます。 T4リガ-ゼは、DNAおよびRANのニックの修復に活発に関与しています。
構成
T4 DNA Ligase is supplied in a solution containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 50 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT, and 50% (v/v) glycerol.
単位の定義
1 Weiss unitは、37°C、20分間に、ノーリット吸着性物質として、1 nmolのP32をピロリン酸からATPに交換する反応を触媒するために必要な酵素量と定義されています。
その他情報
T4 DNAリガーゼは、65°Cで 10分間加熱すると不活化されます。
関連製品
製品番号
詳細
価格
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Resp. Sens. 1
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
D2886PROC:
D2886-100UN-KC:
D2886-100UN:
D2886-500UN:
D2886-VAR:
D2886-BULK:
D2886-BULK-LBL:
D2886-300UN:
D2886-250UN-KC:
D2886-125UN:
D2886-500UN-KC:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Adam B Robertson et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 287(39), 32953-32966 (2012-08-01)
The Escherichia coli very short patch (VSP) repair pathway corrects thymidine-guanine mismatches that result from spontaneous hydrolytic deamination damage of 5-methyl cytosine. The VSP repair pathway requires the Vsr endonuclease, DNA polymerase I, a DNA ligase, MutS, and MutL to
Justin L Sparks et al.
Molecular cell, 47(6), 980-986 (2012-08-07)
Ribonucleotides are incorporated into DNA by the replicative DNA polymerases at frequencies of about 2 per kb, which makes them by far the most abundant form of potential DNA damage in the cell. Their removal is essential for restoring a
Athena Kantartzis et al.
Cell reports, 2(2), 216-222 (2012-09-04)
Trinucleotide repeat (TNR) expansions are the underlying cause of more than 40 neurodegenerative and neuromuscular diseases, including myotonic dystrophy and Huntington's disease. Although genetic evidence points to errors in DNA replication and/or repair as the cause of these diseases, clear
Sambrook, J., et al.
Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 1-1 (1989)
Ayako Nishizawa-Yokoi et al.
The New phytologist, 196(4), 1048-1059 (2012-10-12)
Evidence for the involvement of the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway in Agrobacterium-mediated transferred DNA (T-DNA) integration into the genome of the model plant Arabidopsis remains inconclusive. Having established a rapid and highly efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system in rice (Oryza
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)