おすすめの製品
リコンビナント
expressed in corn
品質水準
形状
liquid
比活性
0.13 U/mg
環境により配慮した代替製品の特徴
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
環境により配慮した代替製品カテゴリ
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−20°C
関連するカテゴリー
詳細
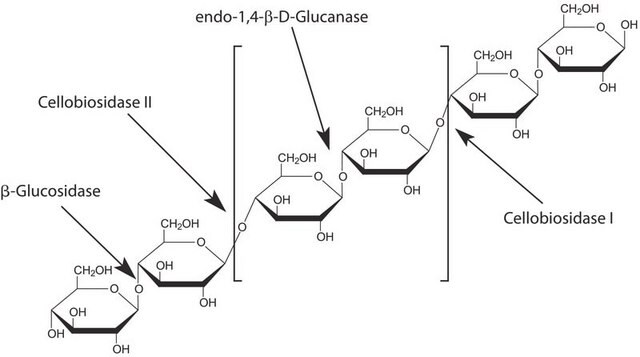
Cellubiohydrolase I is an enzyme present in many fungi, but particularly wood rot fungi. It is a monomer of 53 kDa with a catalytic domain and a cellulose binding domain. The reaction adds water to the glucose bonds in cellulose (non-reducing ends of the chain), yielding cellobiose.
We are committed to bringing you Greener Alternative Products, which adhere to one or more of The 12 Principles of Greener Chemistry. This product has been enhanced for energy efficiency. Find details here.
アプリケーション
Cellobiohydrolase I can be used in combination with endocellulases and b-glucosidase to produce glucose from cellulose.
生物化学的/生理学的作用
Cellobiohydrolase (CBH) is a cellulase which degrades cellulose by hydrolysing the 1,4-β-D-glycosidic bonds. CBH is an exocellulase which cleaves two to four units from the ends of cellulose. CBH I cleaves progressively from the reducing end. CBH I is commonly used in detergents for cleaning textiles. Its ezymatic activity ranges from 37° C to 50° C, with its optimal temperature being approximately 45° C. The optimum pH for the enzyme is 5-6.
単位の定義
Unit Definition: A unit will turn over 1 nmole of methyl-umbelliferyl beta-D cellobioside per min at pH 5 at 50° C.
物理的形状
Provided as an ammonium sulfate precipitate with the source as recombinant maize.
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Resp. Sens. 1
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
E6412-BULK:
E6412-VAR:
E6412-100UN:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Nicolaj Cruys-Bagger et al.
Biotechnology and bioengineering, 109(12), 3199-3204 (2012-07-07)
An amperometric enzyme biosensor for continuous detection of cellobiose has been implemented as an enzyme assay for cellulases. We show that the initial kinetics for cellobiohydrolase I, Cel7A from Trichoderma reesei, acting on different types of cellulose substrates, semi-crystalline and
Zachary K Haviland et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 297(3), 101029-101029 (2021-08-03)
Understanding the mechanism by which cellulases from bacteria, fungi, and protozoans catalyze the digestion of lignocellulose is important for developing cost-effective strategies for bioethanol production. Cel7A from the fungus Trichoderma reesei is a model exoglucanase that degrades cellulose strands from
Oren Yaniv et al.
Acta crystallographica. Section D, Biological crystallography, 68(Pt 7), 819-828 (2012-07-04)
The crystal structure of the family 3b carbohydrate-binding module (CBM3b) of the cellulosomal multimodular hydrolytic enzyme cellobiohydrolase 9A (Cbh9A) from Clostridium thermocellum has been determined. Cbh9A CBM3b crystallized in space group P4(1) with four molecules in the asymmetric unit and
Larissa C Textor et al.
The FEBS journal, 280(1), 56-69 (2012-11-02)
Aiming to contribute toward the characterization of new, biotechnologically relevant cellulolytic enzymes, we report here the first crystal structure of the catalytic core domain of Cel7A (cellobiohydrolase I) from the filamentous fungus Trichoderma harzianum IOC 3844. Our structural studies and
Svein J Horn et al.
Methods in enzymology, 510, 69-95 (2012-05-23)
Natural cellulolytic enzyme systems as well as leading commercial cellulase cocktails are dominated by enzymes that degrade cellulose chains in a processive manner. Despite the abundance of processivity among natural cellulases, the molecular basis as well as the biotechnological implications
資料
Uncover more about glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans including the structure of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), the different types of GAGs, and their functions.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)