おすすめの製品
由来生物
rabbit
品質水準
結合体
unconjugated
抗体製品の状態
IgG fraction of antiserum
抗体製品タイプ
primary antibodies
クローン
polyclonal
形状
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
antigen ~134 kDa
化学種の反応性
human, mouse
テクニック
immunoprecipitation (IP): 5-10 μg using RIPA extract of 500 μg of 293T cells expressing recombinant mouse HDAC6.
microarray: suitable
western blot: 1:1,000 using 293T cells expressing recombinant mouse HDAC6 in a chemiluminescent detection system.
UniProtアクセッション番号
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−20°C
ターゲットの翻訳後修飾
unmodified
遺伝子情報
human ... HDAC6(10013)
mouse ... Hdac6(15185)
詳細
Anti-Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6), is produced in rabbit using a synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acid residues 1199-1213 of human HDAC6. Mammalian HDACs can be divided into three classes according to sequence homology. Class I consists of the yeast Rpd3-like proteins HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3 and HDAC8. Class II consists of the yeast Hda1-like proteins HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC6, HDAC7, HDAC9 and HDAC10. Class III consists of the yeast Sir2-like proteins. Class I HDACs are ubiquitously expressed, most class II HDACs are tissue-specific. Class II HDACs are larger than those of class I and their catalytic domain is located in the carboxy-terminal half of the protein. HDAC6 is a unique deacetylase among class II members in that it contains a duplicate of the catalytic domain in its NH2 terminus as well. The deacetylase activity of class II HDACs is regulated by subcellular localization. Endogenous HDAC6 is predominantly cytoplasmic where it associates with microtubules and functions as an a-tubulin deacetylase. HDAC6 contains a conserved zinc finger motif that is probably involved in the regulation of ubiquitination. The gene HDAC6 is mapped to human chromosome Xp11.23.
特異性
Anti-Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) recognizes human and mouse HDAC6 (~134 kDa). Detection of HDAC6 by immunoblotting is specifically inhibited with the immunizing peptide. Additional nonspecific bands of approx. 50 kDa may be detected in various extract preparations.
免疫原
ヒトHDAC6のアミノ酸残基1199~1213に相当する合成ペプチド。相当するマウスの配列は1アミノ酸異なっています。
アプリケーション
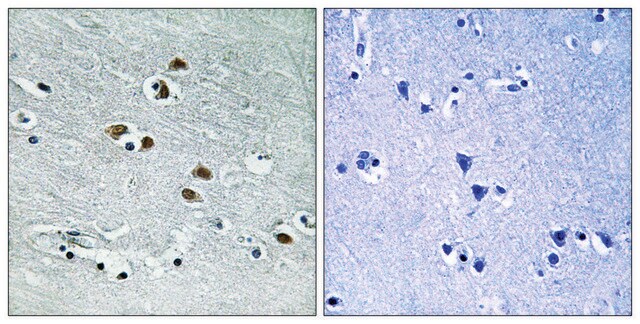
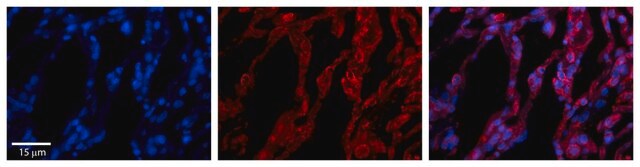
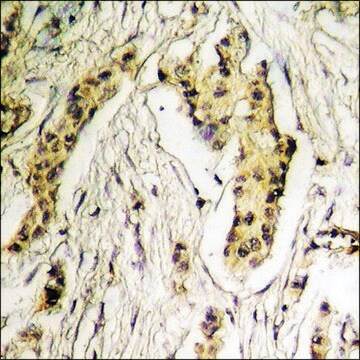
Anti-Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) recognizes human and mouse HDAC6 (~134 kDa). Applications include immunoblotting, immunoprecipitation, immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry.
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Immunohistochemistry (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Immunohistochemistry (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
生物化学的/生理学的作用
Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is an enzyme responsible for deacetylation of histones. HDAC6 is a part of transcriptional corepressor complexes. Overexpression or destruction of HDAC6 may lead to Alzheimer, Parkinson and cardiovascular diseases. Overexpression of HDAC6 is implicated in various cancers like malignant melanoma, lung and bladder cancer. It promotes tumorigenesis, cell migration and invasion. HDAC6 also regulates the expression of critical immune system molecules, targets of chemotherapy like programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1). Mutations in HDAC6 causes X-linked chondrodysplasia.
物理的形状
0.01 M PBS溶液(pH 7.4, 15 mMアジ化ナトリウム含有)。
免責事項
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
適切な製品が見つかりませんか。
製品選択ツール.をお試しください
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Activation of autophagy in mesenchymal stem cells provides tumor stromal support
Sanchez CG, et al.
Carcinogenesis, 32(7), 964-972 (2011)
The class I-specific HDAC inhibitor MS-275 modulates the differentiation potential of mouse embryonic stem cells
Franci G, et al.
Biology Open, 2(10), 1070-1077 (2013)
The human histone deacetylase family
Gray SG and Ekstrom TJ
Experimental Cell Research, 262(2), 75-83 (2001)
Histone deacetylase 6 in cancer
Li T, et al.
Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 11(1), 111-111 (2018)
Ya Hui et al.
iScience, 27(1), 108689-108689 (2024-01-16)
High glucose has been proved to impair cognitive function in type 2 diabetes, but the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we found that high glucose increased transcription factors' SP1 O-GlcNAcylation in regulatory T (Treg) cells. Glycosylated SP1 further enhanced HDAC2
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)