추천 제품
일반 설명
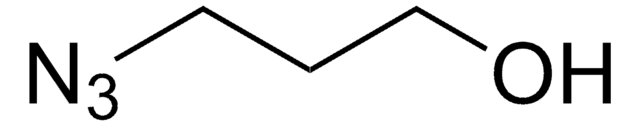
α-Hydroxy-ω-azido terminated-poly(ethylene glycol) is a heterobifunctional PEG derivative that can be used to modify peptides, proteins, or other bioconjugation chemistry applications. PEGylated materials have found broad use in drug delivery systems, virology, and immunology, as the incorporation of PEG improves pharmacological properties such as increased water solubility, enhanced resistance to degradation (protein hydrolysis), increased circulation half-life, and reduced antigenicity. In addition to PEGylation, this heterobifunctional PEG can also be used to form networks for tissue engineering or drug delivery applications due to its dual reactivity.
애플리케이션
α-Hydroxy-ω-azido terminated-poly(ethylene glycol) features two distinct, terminal functional groups: an azide and a hydroxyl group. The terminal azide can undergo copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) or strain promoted azide-alkyne cycloaddition (spAAC), depending on reaction conditions and the identity of the alkyne. In addition, the terminal azide can be reduced to an amine in mild conditions for use in other coupling reactions. The free hydroxyl allows for additional functionalization or a secondary coupling reaction.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
이미 열람한 고객
Sabrina M Hodgson et al.
Biomacromolecules, 17(3), 1093-1100 (2016-02-05)
A series of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels was synthesized using strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloaddition (SPAAC) between PEG chains terminated with either aza-dibenzocyclooctynes or azide functionalities. The gelation process was found to occur rapidly upon mixing the two components in aqueous solution
Joseph G Plaks et al.
Bioconjugate chemistry, 26(6), 1104-1112 (2015-05-20)
Approaches that allow bioorthogonal and, in turn, site-specific chemical modification of proteins present considerable opportunities for modulating protein activity and stability. However, the development of such approaches that enable site-selective modification of proteins at multiple positions, including internal sites within
Kevin N Sill et al.
Biomacromolecules, 18(6), 1874-1884 (2017-05-06)
Described is the development of a polymeric micelle drug delivery platform that addresses the physical property limitations of many nanovectors. The system employs triblock copolymers comprised of a hydrophilic poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) block, and two poly(amino acid) (PAA) blocks: a
Ian W Hamley
Biomacromolecules, 15(5), 1543-1559 (2014-04-12)
The remarkable diversity of the self-assembly behavior of PEG-peptides is reviewed, including self-assemblies formed by PEG-peptides with β-sheet and α-helical (coiled-coil) peptide sequences. The modes of self-assembly in solution and in the solid state are discussed. Additionally, applications in bionanotechnology
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.




![2-[2-(2-Azidoethoxy)ethoxy]ethanol solution ~0.5 M in tert-butyl methyl ether](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/374/007/eea7ca74-41e4-4aac-af71-c93c37ec0a5a/640/eea7ca74-41e4-4aac-af71-c93c37ec0a5a.png)