추천 제품
생물학적 소스
rabbit
Quality Level
결합
unconjugated
항체 형태
affinity isolated antibody
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
polyclonal
양식
buffered aqueous solution
분자량
antigen ~129 kDa
종 반응성
mouse, human
향상된 검증
recombinant expression
Learn more about Antibody Enhanced Validation
농도
~1.5 mg/mL
기술
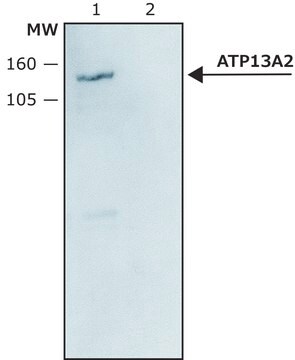
western blot: 1.5-3.0 μg/mL using mouse brain extract (S1 fraction) or HEK-293T cells expressing human ATP13A2
UniProt 수납 번호
배송 상태
dry ice
저장 온도
−20°C
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
유전자 정보
human ... ATP13A2(23400)
일반 설명
ATP13A2 (ATPase type 13A2, also known as PARK9) is a neuronal P-type ATPase of the P5 subfamily. It is present in the lysosome of transiently transfected cells, whereas the unstable truncated mutants are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum and degraded by the proteasome.
ATP13A2 is a member of the P5 subfamily of P-type transport ATPases which include ATP13A1-ATP13A5. Mutations in ATP3A2 also known as PARK9 are associated with hereditary Parkinson′s disease.
Rabbit anti-ATP13A2 (C-terminal region) antibody is specific for human and mouse ATP13A2. Staining of the ATP13A2 band by immunoblotting is specifically inhibited by the ATP13A2 immunizing peptide.
애플리케이션
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Rabbit anti-ATP13A2 (C-terminal region) antibody has been used for western blotting applications at a dilution of 1:1000.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
ATP13A2 (ATPase type 13A2, also known as PARK9) shows elevated expression levels in the brains of sporadic Parkinson′s disease (PD) patients, suggesting a potential role in the more common forms of PD. It is associated with Kufor-Rakeb syndrome (KRS). KRS is a rare form of hereditary PD with juvenile onset. In addition to typical signs of PD, affected individuals show symptoms of more widespread pyramidal neurodegeneration, including dementia.
물리적 형태
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
면책조항
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
시험 성적서(COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Hereditary parkinsonism with dementia is caused by mutations in ATP13A2, encoding a lysosomal type 5 P-type ATPase
Ramirez A, et al.
Nature Genetics, 38(10), 1184-1184 (2006)
Alejandro Estrada-Cuzcano et al.
Brain : a journal of neurology, 140(2), 287-305 (2017-02-01)
Hereditary spastic paraplegias are heterogeneous neurodegenerative disorders characterized by progressive spasticity of the lower limbs due to degeneration of the corticospinal motor neurons. In a Bulgarian family with three siblings affected by complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia, we performed whole exome
Shaun Martin et al.
Parkinson's disease, 2016, 9531917-9531917 (2016-04-14)
The late endo-/lysosomal P-type ATPase ATP13A2 (PARK9) is implicated in Parkinson's disease (PD) and Kufor-Rakeb syndrome, early-onset atypical Parkinsonism. ATP13A2 interacts at the N-terminus with the signaling lipids phosphatidic acid (PA) and phosphatidylinositol (3,5) bisphosphate (PI(3,5)P2), which modulate ATP13A2 activity
David Ramonet et al.
Human molecular genetics, 21(8), 1725-1743 (2011-12-22)
Mutations in the ATP13A2 gene (PARK9, OMIM 610513) cause autosomal recessive, juvenile-onset Kufor-Rakeb syndrome and early-onset parkinsonism. ATP13A2 is an uncharacterized protein belonging to the P(5)-type ATPase subfamily that is predicted to regulate the membrane transport of cations. The physiological
Aaron M Gusdon et al.
Neurobiology of disease, 45(3), 962-972 (2011-12-27)
Mitochondrial dysfunction and autophagy are centrally implicated in Parkinson's disease (PD). Mutations in ATP13A2, which encodes a lysosomal P-type ATPase of unknown function, cause a rare, autosomal recessive parkinsonian syndrome. Lysosomes are essential for autophagy, and autophagic clearance of dysfunctional
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.