추천 제품
생물학적 소스
mouse
Quality Level
결합
unconjugated
항체 형태
ascites fluid
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
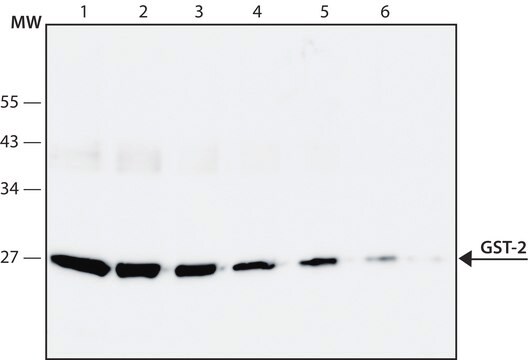
GST-2, monoclonal
포함
15 mM sodium azide
기술
dot blot: suitable
indirect ELISA: suitable
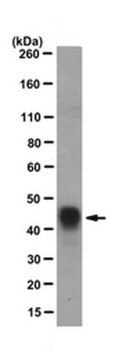
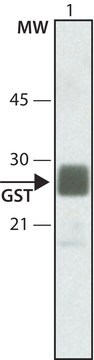
western blot: 1:1,000 using purified recombinant GST or lysate of induced bacteria expressing recombinant GST
동형
IgG2b
배송 상태
dry ice
저장 온도
−20°C
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
일반 설명
Monoclonal anti-glutathione-S-transferase (GST) (mouse IgG2b isotype) is derived from the GST-2 hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from a BALB/c mouse immunized with a purified recombinant GST fusion protein.GST belongs to three family of proteins distinguished as cytosolic, mitochondrial and microsomal GST. At present, eight distinct classes of the soluble cytoplasmic mammalian glutathione S-transferases have been identified: α, κ, μ, ω, σ, θ, π and ζ.
Recombinant target proteins are often expressed as a fusion product with Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST) tags using various expression vector constructs. Thus, antibodies directed against the GST tags of the recombinant constructs can facilitate the purification and study of target proteins. Monoclonal Anti-Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST) antibody reacts with GST from Schistosoma japonicum. Furthermore, the product identifies native as well as denatured-reduced forms of purified GST and GST fusion proteins. The antibody does not detect GST derived from rat, rabbit, porcine and bovine liver or from human placenta.
면역원
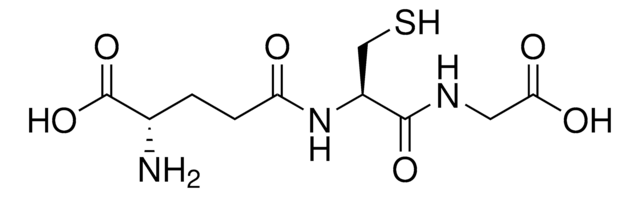
recombinant Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST) fusion protein.
애플리케이션
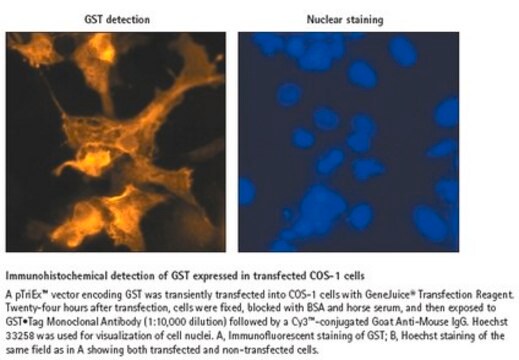
Monoclonal Anti-Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST) antibody has been used for use in western blot and ELISA. This product has also been used for dot blot.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are a family of enzymes that play an important role in detoxification by catalyzing the conjugation of many hydrophobic and electrophilic compounds with reduced glutathione.
면책조항
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
시험 성적서(COA)
Lot/Batch Number
이미 열람한 고객
Marie Brázdová et al.
PloS one, 8(3), e59567-e59567 (2013-04-05)
Hot spot mutant p53 (mutp53) proteins exert oncogenic gain-of-function activities. Binding of mutp53 to DNA is assumed to be involved in mutp53-mediated repression or activation of several mutp53 target genes. To investigate the importance of DNA topology on mutp53-DNA recognition
Claudia Ester et al.
BMC biochemistry, 9, 29-29 (2008-11-19)
The FF domain is conserved across all eukaryotes and usually acts as an adaptor module in RNA metabolism and transcription. Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes two FF domain proteins, Prp40, a component of the U1 snRNP, and Ypr152c, a protein of unknown
Maria Jose Martin et al.
Nucleic acids research, 41(4), 2428-2436 (2013-01-01)
Human DNA polymerase mu (Polμ), a family X member involved in DNA repair, has both template-directed and terminal transferase (template-independent) activities. In addition to their ability to incorporate untemplated nucleotides, another similarity between Polµ and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) is
Structure, function and evolution of glutathione transferases: implications for classification of non-mammalian members of an ancient enzyme superfamily.
Sheehan D, et al.
The Biochemical Journal, 360(1), 1-16 (2001)
Jing-Xiang Wu et al.
Nature communications, 6, 8953-8953 (2015-12-03)
The SAD/BRSK kinases participate in various important life processes, including neural development, cell cycle and energy metabolism. Like other members of the AMPK family, SAD contains an N-terminal kinase domain followed by the characteristic UBA and KA1 domains. Here we
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.