추천 제품
생물학적 소스
bacterial (Flavobacterium heparinum)
Quality Level
결합
conjugate (Glucosaminoglycan)
양식
lyophilized powder
특이 활성도
≥100 units/mg protein (enzyme + BSA)
분자량
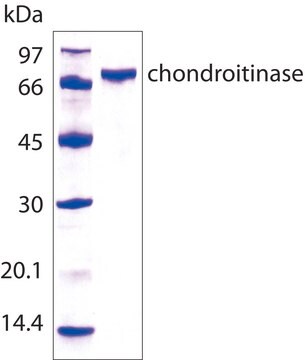
84.1 kDa
저장 온도
−20°C
일반 설명
Heparinase II is one of three key heparin-degrading enzymes of Flavobacterium heparinum (also known as Pedobacter heparinus1). It belongs to the polysaccharide lyases family PL21.
애플리케이션
Heparinase II from Flavobacterium heparinum has been used:
- for digestion of heparin sulfate during exosome isolation
- for digestion of heparin sulfate in notochordal cell conditioned media (NCCM) to investigate the content of glycosaminoglycans in NCCM
- as a component of digestion buffer during cell surface glycan processing
- as a component of heparin lyase (HSase) mix to remove the heparin sulfate on the 293ͰT/ACE2 cell surface and study the effect of histones on the infectivity of pseudovirus
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Heparinase II cleaves heparan sulfate, and to a lesser extent heparin (relative activity about 2:1), at the α (1-4) linkages between hexosamines and uronic acid residues (both glucuronic and iduronic), yielding mainly disaccharides. Heparinase II has the broadest substrate specificity of the three heparinases Heparinase enzymes helps in decoding the complex structures of substrates. Heparin interferes with DNA transcription in PCR and in reverse transcription of RNA. Heparinase II has been used to remove heparin for downstream analysis of genomic DNA.
단위 정의
One unit will form 0.1 μmole of unsaturated uronic acid per hr at pH 7.0 at 25 °C. One International Unit (I.U.) is equivalent to approx. 600 Sigma units.
기타 정보
View more information on enzymes for complex carbohydrate analysis at www.sigma-aldrich.com/enzymeexplorer
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
시험 성적서(COA)
Lot/Batch Number
이미 열람한 고객
David Shaya et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 285(26), 20051-20061 (2010-04-21)
Heparinase II (HepII) is an 85-kDa dimeric enzyme that depolymerizes both heparin and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans through a beta-elimination mechanism. Recently, we determined the crystal structure of HepII from Pedobacter heparinus (previously known as Flavobacterium heparinum) in complex with a
Devina Purmessur et al.
The spine journal : official journal of the North American Spine Society, 15(5), 1060-1069 (2015-02-11)
Painful human intervertebral discs (IVDs) exhibit nerve growth deep into the IVD. Current treatments for discogenic back pain do not address the underlying mechanisms propagating pain and are often highly invasive or only offer temporary symptom relief. The notochord produces
McLean, M.W., et al.
Proc. 8th Int. Symp. Glycoconjugates, 1, 73-73 (1985)
Moffat, C.F., et al.
Proc. 8th Int. Symp. Glycoconjugates, 1, 79-79 (1985)
PCR-sequence-specific primer typing of HLA class I and class II alleles.
Mike Bunce
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 210, 143-171 (2002-11-05)
문서
Uncover more about glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans including the structure of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), the different types of GAGs, and their functions.
Glycosaminoglycans are large linear polysaccharides constructed of repeating disaccharide units.
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.