219096
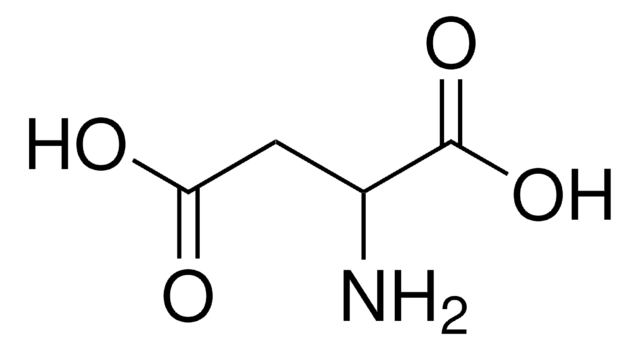
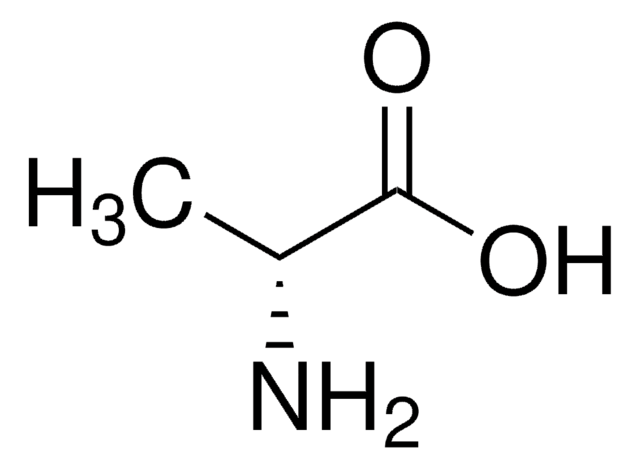
D-Aspartic acid
99%, for peptide synthesis, ReagentPlus®
Synonym(s):
(R)-(−)-Aminosuccinic acid, (R)-2-Aminosuccinic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(3)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Linear Formula:
HO2CCH2CH(NH2)CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
133.10
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
1723529
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Product Name
D-Aspartic acid, ReagentPlus®, 99%
Quality Level
product line
ReagentPlus®
assay
99%
form
powder
optical activity
[α]20/D −24°, c = 2.3 in 6 M HCl
optical purity
ee: 98% (GLC)
reaction suitability
reaction type: solution phase peptide synthesis
mp
>300 °C (lit.)
application(s)
peptide synthesis
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- Metabolomics Analysis Identifies Differential Metabolites as Biomarkers for Acute Myocardial Infarction.: This study utilizes metabolomics to identify biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction, showcasing D-Aspartic acid′s role in amino acid metabolism and potential diagnostic applications. (Zhou et al., 2024).
Legal Information
ReagentPlus is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Takehiko Yokoyama et al.
Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry, 75(8), 1481-1484 (2011-08-09)
Immunohistochemical localization (cellular localization) of endogenous D-aspartate in the marine brown alga Sargassum fusiforme was investigated by the use of a specific polyclonal antibody raised against D-aspartate. D-Aspartate immunoreactivity was evident in the medullary layer in the blade of the
Yuanqi Tao et al.
Analytical chemistry, 84(15), 6814-6820 (2012-07-21)
The presence of a single D-amino acid in a peptide is very difficult to detect. Mass spectrometry-based approaches rely on differences in fragmentation between all L-amino acid-containing peptides and single D-amino acid-containing peptides (which are epimers) for identification. The success
Edi Erwan et al.
Amino acids, 43(5), 1969-1976 (2012-04-03)
Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of L-aspartate (L-Asp) attenuates stress responses in neonatal chicks, but the mechanism has not been clarified. In the present study, three behavioral experiments were carried out under socially isolated stressful conditions exacerbated by the use of corticotrophin-releasing
Yuichi Kaji et al.
The British journal of ophthalmology, 96(8), 1127-1131 (2012-06-15)
Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy (GDLD), also known as familial subepithelial corneal amyloidosis, is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes progressive corneal opacity due to accumulation of amyloid fibrils in the corneal stroma. Genetic analyses have revealed that a mutation in
Yuhei Mori et al.
Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences, 879(29), 3303-3309 (2011-06-04)
UV-B irradiation is one of the risk factors in age-related diseases. We have reported that biologically uncommon D-β-Asp residues accumulate in proteins from sun-exposed elderly human skin. A previous study also reported that carboxymethyl lysine (CML; one of the advanced
Chromatograms
application for HPLCOur team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service