771465
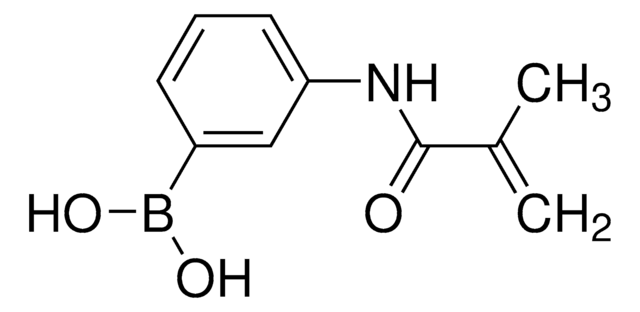
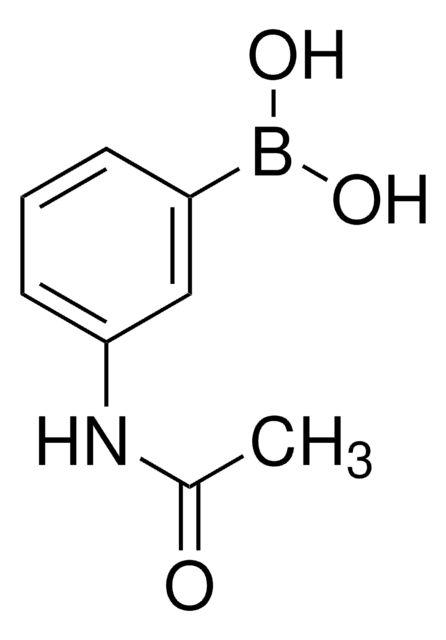
3-(Acrylamido)phenylboronic acid
98%
Synonym(s):
3-(Propenamido)phenylboronic acid, N-Acryloyl-3-aminophenylboronic acid, Boronic acid acrylamide, Phenylboronate acrylamide
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C9H10BNO3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
190.99
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
98%
form
powder
mp
129-146 °C
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
OB(O)c1cccc(NC(=O)C=C)c1
InChI
1S/C9H10BNO3/c1-2-9(12)11-8-5-3-4-7(6-8)10(13)14/h2-6,13-14H,1H2,(H,11,12)
InChI key
ULVXDHIJOKEBMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
3-(Acrylamido)phenylboronic acid(AAPBA) belongs to the class of boronic acid monomers. The boronic acid group (-B(OH)₂)possesses the unique ability to form reversible covalent bonds with certain molecules, such as diols or sugars. This property allows for the design of molecular sensors for detecting and quantifying specific analytes, including carbohydrates and biomolecules. The acrylamido group provides hydrophilic characteristics, making it more suitable for drug delivery applications. It is also utilized as a building block to synthesize boronic acid-based polymers or copolymers for biomedical engineering, and biosensors for glucose monitoring.
Application
3-(Acrylamido)phenylboronic acid can be used as:
- As a monomer to synthesize poly(methacrylic acid)-co-3-(acrylamido)phenylboronic acid (PMAA-co-AAPBA) copolymer as a supramolecular receptor for biosensor applications. AAPBA helps to enhance the water solubility and binding affinity of the copolymer. This copolymer is utilized for carbohydrate sensing in an aqueous medium.
- As a monomer to prepare poly(3-Acrylamidophenyl boronic acid-b-diethylene glycol dimethacrylate) for the fabrication of glucose-sensitive nanoparticles for insulin delivery. The specific interactions of AAPBA with the diol moiety present in glucose molecules induce glucose responsiveness into the block copolymer.
- As a monomer and cross-linker to synthesize self-healing composite hydrogels for tissue engineering and drug delivery systems. They can mimic the properties of natural tissues and provide a suitable environment for cell growth. AAPBA polymerizes with acrylamide and simultaneously interacts with cis-diol of hydroxypropyl guar gum (HPG) to facilitate the formation of hydrogel with good mechanical strength and fast self-healing properties.
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Xiaoyun Wang et al.
RNA (New York, N.Y.), 24(10), 1305-1313 (2018-07-05)
Eukaryotic transfer RNAs (tRNA) contain on average 13 modifications that perform a wide range of roles in translation and in the generation of tRNA fragments that regulate gene expression. Queuosine (Q) modification occurs in the wobble anticodon position of tRNAs
Jun Ding et al.
Plant methods, 9, 13-13 (2013-04-19)
Brassinosteriods (BRs), a group of important phytohormones, have various effects on plant growth and development. However, their physiological functions in plants have not been fully understood to date. Endogenous BRs in plant tissue are extremely low and the elucidation of
Self-healing hydroxypropyl guar gum/poly (acrylamide-co-3-acrylamidophenyl boronic acid) composite hydrogels with yield phenomenon based on dynamic PBA ester bonds and H-bond
Xueting Lu, et al.
Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 561, 325-331 (2019)
Kataoka; et al.
Macromolecules, 27, 1061-1062 (1994)
Mohamed Elsherif et al.
ACS nano, 12(6), 5452-5462 (2018-05-12)
Low-cost, robust, and reusable continuous glucose monitoring systems that can provide quantitative measurements at point-of-care settings is an unmet medical need. Optical glucose sensors require complex and time-consuming fabrication processes, and their readouts are not practical for quantitative analyses. Here
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service