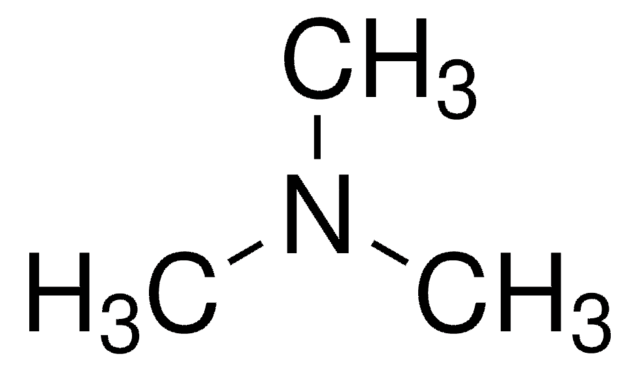
901609
Diisopropylcarbodiimide solution
1 M in dichloromethane
Synonym(s):
Diisopropylmethanediimine
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
liquid
reaction suitability
reaction type: Coupling Reactions
concentration
1 M in dichloromethane
refractive index
n/D 1.4251
density
1.2231
application(s)
peptide synthesis
InChI
1S/C7H14N2/c1-6(2)8-5-9-7(3)4/h6-7H,1-4H3
InChI key
BDNKZNFMNDZQMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Alternative to dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in peptide synthesis.
- Coupling reagent for peptide syntheses.
- DIC (N,N′-Diisopropylcarbodiimide) has been used in combination with 1-hydroxy-7-azabenzotriazole (HOAt) for the coupling of amino acid with N-allylglycine to form N-allylpeptide.
related product
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Carc. 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Central nervous system
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
91.4 °F
flash_point_c
33 °C
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service