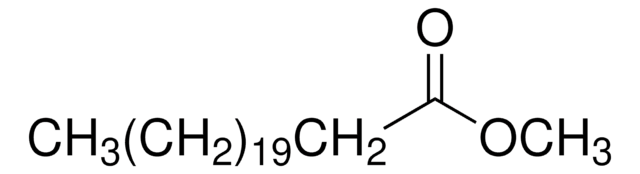10941
Methyl arachidate
analytical standard
Synonym(s):
Arachidic Acid Methyl Ester, Eicosanoic acid, methyl ester, Icosanoic Acid Methyl Ester, Methyl icosanoate, Arachidic acid methyl ester, Methyl eicosanoate
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
analytical standard
Quality Level
assay
≥99.0% (GC)
shelf life
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
bp
215-216 °C/10 mmHg (lit.)
mp
45-48 °C (lit.)
46-49 °C
format
neat
functional group
ester
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC
InChI
1S/C21H42O2/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20-21(22)23-2/h3-20H2,1-2H3
InChI key
QGBRLVONZXHAKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Comparative analysis of gas chromatography-combustion-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-flame ionization detector methods for the determination of fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) in biodiesel samples
- Gas chromatography-tandem differential mobility spectrometry (DMS) based separation and quantification of 16 methyl- and ethyl- fatty acid esters from biodiesel samples
- Analysis of coffee oil and residue obtained from roasted coffee beans to determine the composition of 11 fatty acids following their methyl esterification by gas chromatography coupled with a flame ionization detector (GC-FID)
- Separation and quantification of eight fatty acids after their derivatization to methyl esters in the oil extracted from the leaves of Abutilon hirtum (Lam.) by GC-MS
- Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) based microanalysis of orchid seeds using direct transesterification for the determination of fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs)
Other Notes
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service